Pneumonitis in Patients Treated With Anti-Programmed Death-1/Programmed Death Ligand 1 Therapy
- PMID: 27646942
- PMCID: PMC5559901
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2016.68.2005
Pneumonitis in Patients Treated With Anti-Programmed Death-1/Programmed Death Ligand 1 Therapy
Erratum in
-
Errata.J Clin Oncol. 2017 Aug 1;35(22):2590. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.74.5042. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28750185 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
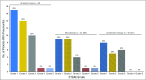
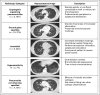
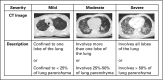
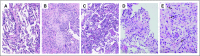
Purpose Pneumonitis is an uncommon but potentially fatal toxicity of anti-programmed death-1 (PD-1)/programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). Clinical, radiologic, and pathologic features are poorly described. Methods Patients who received anti-PD-1/PD-L1 monotherapy or in combination with anti-cytotoxic T-cell lymphocyte-4 mAb were identified at two institutions (Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center: advanced solid cancers, 2009 to 2014, and Melanoma Institute of Australia: melanomas only, 2013 to 2015). Pneumonitis was diagnosed by the treating investigator; cases with confirmed malignant lung infiltration or infection were excluded. Clinical, radiologic, and pathologic features of pneumonitis were collected. Associations among pneumonitis incidence, therapy received, and underlying malignancy were examined with Fisher's exact test as were associations between pneumonitis features and outcomes. Results Of 915 patients who received anti-PD-1/PD-L1 mAbs, pneumonitis developed in 43 (5%; 95% CI, 3% to 6%; Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, 27 of 578 [5%]; Melanoma Institute of Australia, 16 of 337 [5%]). Time to onset of pneumonitis ranged from 9 days to 19.2 months. The incidence of pneumonitis was higher with combination immunotherapy versus monotherapy (19 of 199 [10%] v 24 of 716 [3%]; P < .01). Incidence was similar in patients with melanoma and non-small-cell lung cancer (overall, 26 of 532 [5%] v nine of 209 [4%]; monotherapy, 15 of 417 v five of 152 [ P = 1.0]; combination, 11 of 115 v four of 57 [ P = .78]). Seventy-two percent (31 of 43) of cases were grade 1 to 2, and 86% (37 of 43) improved/resolved with drug holding/immunosuppression. Five patients worsened clinically and died during the course of pneumonitis treatment; proximal cause of death was pneumonitis (n = 1), infection related to immunosuppression (n = 3), or progressive cancer (n = 1). Radiologic and pathologic features of pneumonitis were diverse. Conclusion Pneumonitis associated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 mAbs is a toxicity of variable onset and clinical, radiologic, and pathologic appearances. It is more common when anti-PD-1/PD-L1 mAbs are combined with anti-cytotoxic T-cell lymphocyte-4 mAb. Most events are low grade and improve/resolve with drug holding/immunosuppression. Rarely, pneumonitis worsens despite immunosuppression, and may result in infection and/or death.
Figures

Comment in
-
Programmed Death-1/Programmed Death Ligand-1 Inhibitor-Related Pneumonitis and Radiographic Patterns.J Clin Oncol. 2017 May 10;35(14):1628-1629. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.71.0434. Epub 2017 Feb 6. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28165902 No abstract available.
-
Reply to M. Nishino et al.J Clin Oncol. 2017 May 10;35(14):1629-1630. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.71.6639. Epub 2017 Feb 6. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28165907 No abstract available.
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-related Pneumonitis. Incidence, Risk Factors, and Clinical and Radiographic Features.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018 Oct 1;198(7):951-953. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201803-0525RR. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018. PMID: 30095979 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Weber JS, D’Angelo SP, Minor D, et al. Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma who progressed after anti-CTLA-4 treatment (CheckMate 037): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:375–384. - PubMed
-
- Robert C, Ribas A, Wolchok JD, et al. Anti-programmed-death-receptor-1 treatment with pembrolizumab in ipilimumab-refractory advanced melanoma: A randomised dose-comparison cohort of a phase 1 trial. Lancet. 2014;384:1109–1117. - PubMed
-
- Garon EB, Rizvi NA, Hui R, et al. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2018–2028. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

