A randomized, double blind placebo controlled study of efficacy and tolerability of Withaina somnifera extracts in knee joint pain
- PMID: 27647541
- PMCID: PMC5052364
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaim.2016.05.003
A randomized, double blind placebo controlled study of efficacy and tolerability of Withaina somnifera extracts in knee joint pain
Abstract
Background: Root extracts of Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) are known to possess analgesic, anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective effects. An aqueous extract of roots plus leaves of this plant has shown to yield higher percentages of withanolide glycosides and, accordingly, may possess better analgesic, anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective effects than root alone extracts.
Objectives: To evaluate efficacy and tolerability of a standardized aqueous extract of roots plus leaves of W. somnifera in patients with knee joint pain and discomfort.
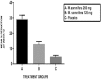
Material and methods: Sixty patients with knee joint pain and discomfort were randomized in a double-blind manner to W. somnifera 250 mg, W. somnifera 125 mg and placebo, all given twice daily. Assessment was done by Modified WOMAC, Knee Swelling Index (KSI), Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) at baseline and at the end of 4, 8, 12 weeks. Tolerability was assessed by incidence of adverse effects in treatment groups. Student's 't' test and ANOVA were used to compare mean change from baseline within and between the study groups. A p < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results: At the end of 12 weeks, compared to baseline and placebo, significant reductions were observed in mean mWOMAC and KSI in W. somnifera 250 mg (p < 0.001), W. somnifera 125 mg (p < 0.05) groups. VAS scores for pain, stiffness and disability were significantly reduced in W. somnifera 250 mg (p < 0.001), W. somnifera 125 mg (p < 0.01) groups. W. somnifera 250 mg group showed earliest efficacy (at 4 weeks). All treatments were well tolerated.
Conclusions: Both the doses of an aqueous extract of W. somnifera produced significant reduction in outcome variables, with the 250 mg group showing significantly better response. In addition, the therapeutic response appears to be dose-dependent and free of any significant GI disturbances.
Keywords: Ashwagandha; Knee joint; WOMAC; Withania somnifera.
Copyright © 2016 Transdisciplinary University, Bangalore and World Ayurveda Foundation. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the efficacy of Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) root extract in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial.Complement Ther Med. 2016 Aug;27:25-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2016.03.018. Epub 2016 Apr 9. Complement Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27515872 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of dietary supplementation with a standardized aqueous extract of Terminalia chebula fruit (AyuFlex®) on joint mobility, comfort, and functional capacity in healthy overweight subjects: a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Oct 2;17(1):475. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1977-8. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28969626 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Antihyperalgesic effects of ashwagandha (Withania somnifera root extract) in rat models of postoperative and neuropathic pain.Inflammopharmacology. 2018 Feb;26(1):207-215. doi: 10.1007/s10787-017-0389-1. Epub 2017 Aug 28. Inflammopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 28849547
-
A critical assessment of the whole plant-based phytotherapeutics from Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal with respect to safety and efficacy vis-a-vis leaf or root extract-based formulation.Toxicol Mech Methods. 2023 Oct;33(8):698-706. doi: 10.1080/15376516.2023.2242933. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2023. PMID: 37533233 Review.
-
A systematic review of the clinical use of Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) to ameliorate cognitive dysfunction.Phytother Res. 2020 Mar;34(3):583-590. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6552. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Phytother Res. 2020. PMID: 31742775
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of Enriched Milk with Ashwagandha Extract and Tryptophan for Improving Subjective Sleep Quality in Adults with Sleep Problems: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial.Clocks Sleep. 2024 Aug 9;6(3):417-432. doi: 10.3390/clockssleep6030028. Clocks Sleep. 2024. PMID: 39189195 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) on VO2max: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Nutrients. 2020 Apr 17;12(4):1119. doi: 10.3390/nu12041119. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32316411 Free PMC article.
-
The Biota orientalis, oil extract Epiitalis®, is efficacious at reducing the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis: a pilot, multi-site, dose-ranging, randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled trial.Inflammopharmacology. 2022 Aug;30(4):1323-1334. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-01013-y. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Inflammopharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35732989 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Natural Products as Sources of Novel Drug Candidates for the Pharmacological Management of Osteoarthritis: A Narrative Review.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2019 Nov 1;27(6):503-513. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2019.139. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2019. PMID: 31646842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative analysis of medicinal plants used to treat musculoskeletal ailments by non-institutionally trained siddha practitioners of Virudhunagar district, Tamil Nadu, India.J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2021 Jan-Mar;12(1):58-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jaim.2018.11.005. Epub 2019 Apr 16. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2021. PMID: 31003860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO; Geneva: 2002. World health report 2002. Reducing risks, Promoting Healthy Life. - PubMed
-
- Saloni Tanna, Osteoarthritis: Opportunities to Address Pharmaceutical Gaps; 7 October 2004; Priority Medicines for Europe and the World; “A Public Health Approach to Innovation” – Background Paper available on http://archives.who.int/prioritymeds/report/background/osteoarthritis.doc (accessed on 31st August 2016).
-
- Australian Orthopaedic Association . 2009. Hip and knee arthroplasty. Natl Jt Replace Regist Annu Rep 2009.
-
- Jordan K.M., Arden N.K., Doherty M., Bannwarth B. EULAR Recommendations 2003: An evidence based approach to the Management of knee osteoarthritis: report of a task force of the standing committee for international clinical studies including therapeutic trials (ESCISIT) Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62:1145–1155. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tramer M.R., Moore R.A., Reynolds D.J., McQuay H.J. Quantitative estimation of rare adverse events which follow a biological progression: a new model applied to chronic NSAID use. Pain. 2000;85:169–182. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

