Creative females have larger white matter structures: Evidence from a large sample study
- PMID: 27647672
- PMCID: PMC6866835
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.23369
Creative females have larger white matter structures: Evidence from a large sample study
Abstract
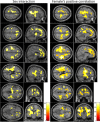
The importance of brain connectivity for creativity has been theoretically suggested and empirically demonstrated. Studies have shown sex differences in creativity measured by divergent thinking (CMDT) as well as sex differences in the structural correlates of CMDT. However, the relationships between regional white matter volume (rWMV) and CMDT and associated sex differences have never been directly investigated. In addition, structural studies have shown poor replicability and inaccuracy of multiple comparisons over the whole brain. To address these issues, we used the data from a large sample of healthy young adults (776 males and 560 females; mean age: 20.8 years, SD = 0.8). We investigated the relationship between CMDT and WMV using the newest version of voxel-based morphometry (VBM). We corrected for multiple comparisons over whole brain using the permutation-based method, which is known to be quite accurate and robust. Significant positive correlations between rWMV and CMDT scores were observed in widespread areas below the neocortex specifically in females. These associations with CMDT were not observed in analyses of fractional anisotropy using diffusion tensor imaging. Using rigorous methods, our findings further supported the importance of brain connectivity for creativity as well as its female-specific association. Hum Brain Mapp 38:414-430, 2017. © 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: creativity; sex difference; structural connectivity; voxel-based morphometry; white matter.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Convergent creative thinking performance is associated with white matter structures: Evidence from a large sample study.Neuroimage. 2020 Apr 15;210:116577. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.116577. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Neuroimage. 2020. PMID: 31978544
-
Regional homogeneity, resting-state functional connectivity and amplitude of low frequency fluctuation associated with creativity measured by divergent thinking in a sex-specific manner.Neuroimage. 2017 May 15;152:258-269. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.02.079. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Neuroimage. 2017. PMID: 28257930
-
White matter structures associated with creativity: evidence from diffusion tensor imaging.Neuroimage. 2010 May 15;51(1):11-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.02.035. Epub 2010 Feb 17. Neuroimage. 2010. PMID: 20171286
-
Sex-specific intra- and inter-hemispheric structural connectivity related to divergent thinking.Neurosci Lett. 2022 Mar 23;774:136513. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2022.136513. Epub 2022 Feb 8. Neurosci Lett. 2022. PMID: 35149199
-
Polygenic risk score for bipolar disorder associates with divergent thinking and brain structures in the prefrontal cortex.Hum Brain Mapp. 2021 Dec 15;42(18):6028-6037. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25667. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Hum Brain Mapp. 2021. PMID: 34587347 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of Time-Compressed Speech Training on Multiple Functional and Structural Neural Mechanisms Involving the Left Superior Temporal Gyrus.Neural Plast. 2018 Feb 20;2018:6574178. doi: 10.1155/2018/6574178. eCollection 2018. Neural Plast. 2018. PMID: 29675038 Free PMC article.
-
Brain White Matter Correlates of Creativity in Schizophrenia: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study.Front Neurosci. 2020 Jun 23;14:572. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00572. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32655352 Free PMC article.
-
Network Neuroscience of Creative Cognition: Mapping Cognitive Mechanisms and Individual Differences in the Creative Brain.Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2019 Jun;27:22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.cobeha.2018.08.013. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2019. PMID: 30906824 Free PMC article.
-
Sex influences the brain functional connectivity correlates of originality.Sci Rep. 2021 Dec 2;11(1):23269. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02674-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34857822 Free PMC article.
-
Childhood socioeconomic status is associated with psychometric intelligence and microstructural brain development.Commun Biol. 2021 Apr 29;4(1):470. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-01974-w. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 33927305 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham A (2016): Gender and creativity: An overview of psychological and neuroscientific literature. Brain Imaging Behav 10:609–618. - PubMed
-
- Abraham A, Thybusch K, Pieritz K, Hermann C (2014): Gender differences in creative thinking: Behavioral and fMRI findings. Brain Imaging nd Behav 8:39–51. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2000): Voxel‐based morphometry‐the methods. Neuroimage 11:805–821. - PubMed
-
- Baer J, Kaufman JC (2008): Gender differences in creativity. J Creat Behav 42:75–105.
-
- Baldo JV, Shimamura AP, Delis DC, Kramer J, Kaplan E (2001): Verbal and design fluency in patients with frontal lobe lesions. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 7:586–596. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

