Anti-TGF- β 1 Antibody Therapy in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy
- PMID: 27647855
- PMCID: PMC5328150
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2015111230
Anti-TGF- β 1 Antibody Therapy in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy
Abstract
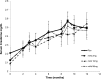
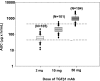
TGF-β has been implicated as a major pathogenic factor in diabetic nephropathy. This randomized, double-blind, phase 2 study assessed whether modulating TGF-β1 activity with a TGF-β1-specific, humanized, neutralizing monoclonal antibody (TGF-β1 mAb) is safe and more effective than placebo in slowing renal function loss in patients with diabetic nephropathy on chronic stable renin-angiotensin system inhibitor treatment. We randomized 416 patients aged ≥25 years with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, a serum creatinine (SCr) level of 1.3-3.3 mg/dl for women and 1.5-3.5 mg/dl for men (or eGFR of 20-60 ml/min per 1.73 m2), and a 24-hour urine protein-to-creatinine ratio ≥800 mg/g to TGF-β1 mAb (2-, 10-, or 50-mg monthly subcutaneous dosing for 12 months) or placebo. We assessed a change in SCr from baseline to 12 months as the primary efficacy variable. Although the Data Monitoring Committee did not identify safety issues, we terminated the trial 4 months early for futility on the basis of their recommendation. The placebo group had a mean±SD change in SCr from baseline to end of treatment of 0.33±0.67 mg/dl. Least squares mean percentage change in SCr from baseline to end of treatment did not differ between placebo (14%; 95% confidence interval [95% CI], 9.7% to 18.2%) and TGF-β1 mAb treatments (20% [95% CI, 15.3% to 24.3%], 19% [95% CI, 14.2% to 23.0%], and 19% [95% CI, 14.0% to 23.3%] for 2-, 10-, and 50-mg doses, respectively). Thus, TGF-β1 mAb added to renin-angiotensin system inhibitors did not slow progression of diabetic nephropathy.
Keywords: Diabetic Kidney Disease; Transforming growth factor beta; proteinuria; renal fibrosis.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- United States Renal Data System : 2014 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States, Bethesda, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2014 - PubMed
-
- International Diabetes Federation : IDF Diabetes Atlas, 6th Ed., Brussels, Belgium, International Diabetes Federation, 2013
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

