Endostatin enhances antitumor effect of tumor antigen-pulsed dendritic cell therapy in mouse xenograft model of lung carcinoma
- PMID: 27647974
- PMCID: PMC5018541
- DOI: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2016.04.09
Endostatin enhances antitumor effect of tumor antigen-pulsed dendritic cell therapy in mouse xenograft model of lung carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the antitumor effect of endostatin combined with tumor antigen-pulsed dendritic cell (DC)-T cell therapy on lung cancer.
Methods: Transplanted Lewis lung cancer (LLC) models of C57BL/6 mice were established by subcutaneous injection of LLC cells in left extremity axillary. Tumor antigen-pulsed DC-T cells from spleen cells and bone of mice were cultured in vitro. Tumor-bearing mice were randomly divided into three groups, including DC-T+endostatin group, DC-T group, and phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) control group. Microvessel density (MVD) of tumor tissue in tumor-bearing mice was determined by immunohistochemistry (IHC). The expressions of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) were determined by Western blotting and IHC staining. The proportions of CD8+ T cells, mature dendritic cells (mDC), tumor-associated macrophages [TAM (M1/M2)], and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) in suspended cells of tumor tissue were determined by flow cytometry. The expressions of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10, IL-17, transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ) in suspended cells of tumor tissue were detected by enzyme-linked immune sorbent assay (ELISA).
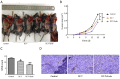
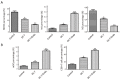
Results: DC-T cells combined with endostatin remarkably suppressed tumor growth. MVD of mice in DC-T+endostatin group was significantly lower than that of the control group and DC-T monotherapy group. The expressions of VEGF, IL-6 and IL-17 in tumors were markedly decreased, but IFN-γ and HIF-1α increased after treating with DC-T cells combined with endostatin, compared to control group and DC-T group. In the DC-T+endostatin group, the proportions of MDSC and TAM (M2 type) were significantly decreased, mDC and TAM (M1 type) were up-regulated, and CD8+ T cells were recruited to infiltrate tumors, in contrast to PBS control and DC-T monotherapy. DC-T cells combined with endostatin potently reduced the expressions of IL-6, IL-10, TGF-β and IL-17 in tumor tissue, and enhanced the expression of IFN-γ.
Conclusions: The study indicated the synergic antitumor effects between endostatin and tumor antigen-pulsed DC-T cells, which may be a prospective therapy strategy to achieve potent antitumor effects on lung cancer.
Keywords: DC-T cells; Endostatin; cellular therapy; lung cancer; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Sharma P, Wagner K, Wolchok JD, et al. Novel cancer immunotherapy agents with survival benefit: recent successes and next steps. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:805–12. doi: 10.1038/nrc3153. [Sharma P, Wagner K, Wolchok JD, et al. Novel cancer immunotherapy agents with survival benefit: recent successes and next steps. Nat Rev Cancer 2011;11:805-12.] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg SA. Overcoming obstacles to the effective immunotherapy of human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:12643–4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0806877105. [Rosenberg SA. Overcoming obstacles to the effective immunotherapy of human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008;105:12643-4.] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
