Preservation of Cognitive Function by Lepidium meyenii (Maca) Is Associated with Improvement of Mitochondrial Activity and Upregulation of Autophagy-Related Proteins in Middle-Aged Mouse Cortex
- PMID: 27648102
- PMCID: PMC5018343
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/4394261
Preservation of Cognitive Function by Lepidium meyenii (Maca) Is Associated with Improvement of Mitochondrial Activity and Upregulation of Autophagy-Related Proteins in Middle-Aged Mouse Cortex
Abstract
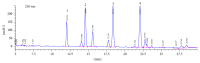
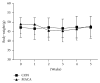
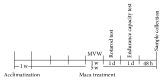
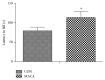
Maca has been used as a foodstuff and a traditional medicine in the Andean region for over 2,000 years. Recently the neuroprotective effects of maca also arouse interest of researchers. Decrease in mitochondrial function and decline in autophagy signaling may participate in the process of age-related cognitive decline. This study aimed to investigate if maca could improve cognitive function of middle-aged mice and if this effect was associated with improvement of mitochondrial activity and modulation of autophagy signaling in mouse cortex. Fourteen-month-old male ICR mice received maca powder administered by gavage for five weeks. Maca improved cognitive function, motor coordination, and endurance capacity in middle-aged mice, accompanied by increased mitochondrial respiratory function and upregulation of autophagy-related proteins in cortex. Our findings suggest that maca is a newly defined nutritional plant which can improve mitochondrial function and upregulate autophagy-related proteins and may be an effective functional food for slowing down age-related cognitive decline.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Influences of dietary supplementation with Lepidium meyenii (Maca) on stallion sperm production and on preservation of sperm quality during storage at 5 °C.Andrology. 2018 Mar;6(2):351-361. doi: 10.1111/andr.12463. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Andrology. 2018. PMID: 29359412 Clinical Trial.
-
Is the hype around the reproductive health claims of maca (Lepidium meyenii Walp.) justified?J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jan 30;211:126-170. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.08.003. Epub 2017 Aug 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28811221 Review.
-
Lepidium meyenii (Maca) enhances the serum levels of luteinising hormone in female rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Feb 3;151(2):897-902. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.11.058. Epub 2013 Dec 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24333960
-
Toxicological aspects of the South American herbs cat's claw (Uncaria tomentosa) and Maca (Lepidium meyenii) : a critical synopsis.Toxicol Rev. 2005;24(1):11-35. doi: 10.2165/00139709-200524010-00002. Toxicol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16042502 Review.
-
Effect of Lepidium meyenii (maca) on testicular function of mice with chemically and physically induced subfertility.Andrologia. 2016 Oct;48(8):927-34. doi: 10.1111/and.12682. Andrologia. 2016. PMID: 27681650
Cited by
-
Macamide B Pretreatment Attenuates Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage of Mice Induced Apoptosis and Regulates Autophagy via the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 May;59(5):2776-2798. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02751-4. Epub 2022 Feb 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35190953
-
Integrated Proteomics and Lipidomics Investigation of the Mechanism Underlying the Neuroprotective Effect of N-benzylhexadecanamide.Molecules. 2018 Nov 9;23(11):2929. doi: 10.3390/molecules23112929. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30424008 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoic acid inhibits cognitive impairment induced by multiple cell phones in young male rats: role of Sirt1 and Atg7 pathway.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 28;13(1):18486. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44134-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37898621 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effect of herbal extracts inhibiting soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) and cyclooxygenase (COX) against chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment in mice.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023 Jul 30;667:64-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.05.008. Epub 2023 May 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023. PMID: 37209564 Free PMC article.
-
Not All Maca Is Created Equal: A Review of Colors, Nutrition, Phytochemicals, and Clinical Uses.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 14;16(4):530. doi: 10.3390/nu16040530. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38398854 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gonzalez G. F., Córdova A., Vega K., Chung A., Villena A., Góñez C. Effect of Lepidium meyenii (Maca), a root with aphrodisiac and fertility-enhancing properties, on serum reproductive hormone levels in adult healthy men. Journal of Endocrinology. 2003;176(1):163–168. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1760163. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brooks N. A., Wilcox G., Walker K. Z., Ashton J. F., Cox M. B., Stojanovska L. Beneficial effects of Lepidium meyenii (Maca) on psychological symptoms and measures of sexual dysfunction in postmenopausal women are not related to estrogen or androgen content. Menopause. 2008;15(6):1157–1162. doi: 10.1097/gme.0b013e3181732953. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Balick M. J., Lee R. Maca: from traditional food crop to energy and libido stimulant. Alternative Therapies in Health and Medicine. 2002;8(2):96–98. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

