Effects of Transcutaneous Electrical Acustimulation on Refractory Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
- PMID: 27648103
- PMCID: PMC5018321
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/8246171
Effects of Transcutaneous Electrical Acustimulation on Refractory Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Abstract
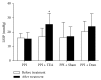
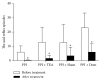
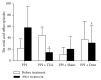
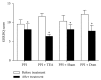
Objective. To investigate effects and possible mechanisms of transcutaneous electrical acustimulation (TEA) performed by a wearable watch-size stimulator for refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease (RGERD). Methods. Twenty patients diagnosed as RGERD were enrolled in the study and randomly divided into four groups: esomeprazole group (Group A), esomeprazole combined with TEA group (Group B), esomeprazole combined with sham-TEA group (Group C), and esomeprazole combined with domperidone group (Group D). HRM and 24 h pH-impedance monitoring and GerdQ score were used to measure related indexes before and after treatment. Results. (1) TEA significantly increased LESP, compared with PPI treatment only or PPI plus sham-TEA. After pairwise comparison, LESP of Group B was increased more than Group A (P = 0.008) or Group C (P = 0.021). (2) PPI plus TEA decreased not only the number of acid reflux episodes but also the number of weak acid reflux episodes (P = 0.005). (3) Heartburn and reflux symptoms were improved more with PPI + TEA than with PPI treatment only or PPI plus sham-TEA (GerdQ scores, P = 0.001). Conclusion. TEA can improve symptoms in RGERD patients by increasing LESP and decreasing events of weak acid reflux and acid reflux; addition of TEA to esomeprazole significantly enhances the effect of TEA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ameliorating Effects of Transcutaneous Electrical Acustimulation Combined With Deep Breathing Training on Refractory Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Mediated via the Autonomic Pathway.Neuromodulation. 2019 Aug;22(6):751-757. doi: 10.1111/ner.13021. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Neuromodulation. 2019. PMID: 31347247 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Elevation of Lower Esophageal Sphincter Pressure With Acute Transcutaneous Electrical Acustimulation Synchronized With Inspiration.Neuromodulation. 2019 Jul;22(5):586-592. doi: 10.1111/ner.12967. Epub 2019 May 28. Neuromodulation. 2019. PMID: 31136053 Clinical Trial.
-
A prospective study to compare a symptom-based reflux disease questionnaire to 48-h wireless pH monitoring for the identification of gastroesophageal reflux (revised 2-26-11).Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep;106(9):1604-11. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2011.180. Epub 2011 Jun 21. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21691342 Clinical Trial.
-
ARE THE PERSISTENT SYMPTOMS TO PROTON PUMP INHIBITOR THERAPY DUE TO REFRACTORY GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE OR TO OTHER DISORDERS?Arq Gastroenterol. 2018 Nov;55Suppl 1(Suppl 1):85-91. doi: 10.1590/S0004-2803.201800000-48. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Arq Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30304291 Review.
-
Impedance-pH Monitoring for Diagnosis of Reflux Disease: New Perspectives.Dig Dis Sci. 2017 Aug;62(8):1881-1889. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4625-8. Epub 2017 May 26. Dig Dis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28550489 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuromodulation for functional upper gastrointestinal diseases.Gut Microbiota Integr Wellness. 2023;1:10.54844/gmiw.2022.0087. doi: 10.54844/gmiw.2022.0087. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Gut Microbiota Integr Wellness. 2023. PMID: 38406297 Free PMC article.
-
Neuromodulation for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review.J Transl Gastroenterol. 2023;1(1):47-56. Epub 2023 Sep 25. J Transl Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 38009094 Free PMC article.
-
Class side effects: decreased pressure in the lower oesophageal and the pyloric sphincters after the administration of dopamine antagonists, neuroleptics, anti-emetics, L-NAME, pentadecapeptide BPC 157 and L-arginine.Inflammopharmacology. 2017 May 17. doi: 10.1007/s10787-017-0358-8. Online ahead of print. Inflammopharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28516373
-
A comparison of the efficacy and safety of complementary and alternative therapies for gastroesophageal reflux disease: A protocol for network meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jul 24;99(30):e21318. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021318. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32791724 Free PMC article.
-
Current complementary and alternative therapy forgastroesophageal reflux disease.Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2023 Oct 4;11:goad057. doi: 10.1093/gastro/goad057. eCollection 2023. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2023. PMID: 37810946 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cho Y. K., Choi M.-G., Park E. Y., et al. Effect of mosapride combined with esomeprazole improves esophageal peristaltic function in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: A study using high resolution manometry. Digestive Diseases and Sciences. 2013;58(4):1035–1041. doi: 10.1007/s10620-012-2430-y. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

