Prognostic significance of MST1R dysregulation in renal cell tumors
- PMID: 27648366
- PMCID: PMC5004080
Prognostic significance of MST1R dysregulation in renal cell tumors
Abstract
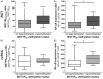
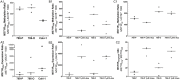
Macrophage stimulating 1 receptor (MST1R) is a C-MET proto-oncogene family receptor tyrosine kinase. Promoter methylation patterns determine transcription of MST1R variants as hypermethylation of a region upstream of transcription start site (TSS) is associated with lack of MST1R long transcript (MST1R long) and expression of a short transcript with oncogenic potential. Thus, we aimed to investigate MST1R variant transcript regulation in renal cell tumors (RCT) and assess their prognostic potential. We found, in a series of 120 RCT comprising the four main subtypes (clear cell, papillary and chromophobe renal cell carcinoma, and oncocytoma), that higher methylation levels close to TSS were associated with total MST1R expression levels (MST1R total) in primary tumors (p=0.049) and renal cancer cell lines. After demethylating treatment, MST1R long/MST1R total ratio increased, as expected, in two renal cell carcinoma cell lines tested. However, in primary tumors with hypermethylation upstream of TSS, a decrease in MST1R long/MST1R total ratio was not detected, although higher expression ratio of nuclear factor-κB was apparent. Furthermore, survival analysis demonstrated that MST1R long/MST1R total ratio was independently associated with shorter disease-specific and disease-free survival, whereas MST1R total expression associated with shorter disease-specific survival. In conclusion, although promoter methylation patterns seem to determine MST1R global transcription regulation in renal cell carcinoma, other mechanisms might contribute to deregulate MST1R variant expression in RCT. Nevertheless, MST1R total expression and MST1R long/MST1R total ratio modulate the biological and clinical aggressiveness of renal cell carcinoma, as depicted by its prognostic significance, a finding that requires validation in a larger independent series.
Keywords: MST1R; MST1R expression; MST1R promoter methylation; RON; Renal cell tumors; epigenetics.
Figures


References
-
- Ronsin C, Muscatelli F, Mattei MG, Breathnach R. A novel putative receptor protein tyrosine kinase of the met family. Oncogene. 1993;8:1195–1202. - PubMed
-
- Yoshimura T, Yuhki N, Wang MH, Skeel A, Leonard EJ. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of human macrophage stimulating protein (MSP, MST1) confirms MSP as a member of the family of kringle proteins and locates the MSP gene on chromosome 3. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:15461–15468. - PubMed
-
- Wang MH, Dlugosz AA, Sun Y, Suda T, Skeel A, Leonard EJ. Macrophage-stimulating protein induces proliferation and migration of murine keratinocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1996;226:39–46. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
