MicroRNA-138 and MicroRNA-25 Down-regulate Mitochondrial Calcium Uniporter, Causing the Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Cancer Phenotype
- PMID: 27648837
- PMCID: PMC5378421
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201604-0814OC
MicroRNA-138 and MicroRNA-25 Down-regulate Mitochondrial Calcium Uniporter, Causing the Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Cancer Phenotype
Abstract
Rationale: Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is an obstructive vasculopathy characterized by excessive pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell (PASMC) proliferation, migration, and apoptosis resistance. This cancer-like phenotype is promoted by increased cytosolic calcium ([Ca2+]cyto), aerobic glycolysis, and mitochondrial fission.
Objectives: To determine how changes in mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) complex (MCUC) function influence mitochondrial dynamics and contribute to PAH's cancer-like phenotype.
Methods: PASMCs were isolated from patients with PAH and healthy control subjects and assessed for expression of MCUC subunits. Manipulation of the pore-forming subunit, MCU, in PASMCs was achieved through small interfering RNA knockdown or MCU plasmid-mediated up-regulation, as well as through modulation of the upstream microRNAs (miRs) miR-138 and miR-25. In vivo, nebulized anti-miRs were administered to rats with monocrotaline-induced PAH.
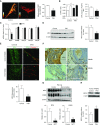
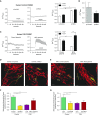
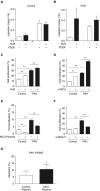
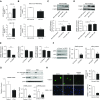
Measurements and main results: Impaired MCUC function, resulting from down-regulation of MCU and up-regulation of an inhibitory subunit, mitochondrial calcium uptake protein 1, is central to PAH's pathogenesis. MCUC dysfunction decreases intramitochondrial calcium ([Ca2+]mito), inhibiting pyruvate dehydrogenase activity and glucose oxidation, while increasing [Ca2+]cyto, promoting proliferation, migration, and fission. In PAH PASMCs, increasing MCU decreases cell migration, proliferation, and apoptosis resistance by lowering [Ca2+]cyto, raising [Ca2+]mito, and inhibiting fission. In normal PASMCs, MCUC inhibition recapitulates the PAH phenotype. In PAH, elevated miRs (notably miR-138) down-regulate MCU directly and also by decreasing MCU's transcriptional regulator cAMP response element-binding protein 1. Nebulized anti-miRs against miR-25 and miR-138 restore MCU expression, reduce cell proliferation, and regress established PAH in the monocrotaline model.
Conclusions: These results highlight miR-mediated MCUC dysfunction as a unifying mechanism in PAH that can be therapeutically targeted.
Keywords: cAMP response element–binding protein; microRNA-25- and -138-5p; mitochondrial calcium uptake protein 1; pyruvate dehydrogenase.
Figures


Comment in
-
Mitochondrial Calcium Transport: A Potentially Prominent, Therapeutically Targetable Contributor to Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Progression.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017 Feb 15;195(4):420-421. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201609-1896ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017. PMID: 28199162 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Thenappan T, Shah SJ, Rich S, Gomberg-Maitland M. A USA-based registry for pulmonary arterial hypertension: 1982-2006. Eur Respir J. 2007;30:1103–1110. - PubMed
-
- Sutendra G, Michelakis ED. The metabolic basis of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Cell Metab. 2014;19:558–573. - PubMed
-
- Marsboom G, Toth PT, Ryan JJ, Hong Z, Wu X, Fang YH, Thenappan T, Piao L, Zhang HJ, Pogoriler J, et al. Dynamin-related protein 1-mediated mitochondrial mitotic fission permits hyperproliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and offers a novel therapeutic target in pulmonary hypertension. Circ Res. 2012;110:1484–1497. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

