Antidepressive and BDNF effects of enriched environment treatment across ages in mice lacking BDNF expression through promoter IV
- PMID: 27648918
- PMCID: PMC5048201
- DOI: 10.1038/tp.2016.160
Antidepressive and BDNF effects of enriched environment treatment across ages in mice lacking BDNF expression through promoter IV
Abstract
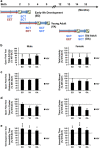
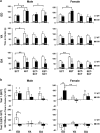
Reduced promoter IV-driven expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is implicated in stress and major depression. We previously reported that defective promoter IV (KIV) caused depression-like behavior in young adult mice, which was reversed more effectively by enriched environment treatment (EET) than antidepressants. The effects of promoter IV-BDNF deficiency and EET over the life stages remain unknown. Since early-life development (ED) involves dynamic epigenetic processes, we hypothesized that EET during ED would provide maximum antidepressive effects that would persist later in life due to enhanced, long-lasting BDNF induction. We tested this hypothesis by determining EET effects across three life stages: ED (0-2 months), young adult (2-4 months), and old adult (12-14 months). KIV mice at all life stages showed depression-like behavior in the open-field and tail-suspension tests compared with wild-type mice. Two months of EET reduced depression-like behavior in ED and young adult, but not old adult mice, with the largest effect in ED KIV mice. This effect lasted for 1 month after discontinuance of EET only in ED mice. BDNF protein induction by EET in the hippocampus and frontal cortex was also the largest in ED mice and persisted only in the hippocampus of ED KIV mice after discontinuance of EET. No gender-specific effects were observed. The results suggest that defective promoter IV causes depression-like behavior, regardless of age and gender, and that EET during ED is particularly beneficial to individuals with promoter IV-BDNF deficiency, while additional treatment may be needed for older adults.
Figures



References
-
- Hebb DO. The effects of early experience on problem-solving at maturity. Am Psychol 1947; 2: 306–307.
-
- Rosenzweig MR. Environmental complexity, cerebral change, and behavior. Am Psychol 1966; 21: 321–332. - PubMed
-
- van Praag H, Kempermann G, Gage FH. Neural consequences of environmental enrichment. Nat Rev Neurosci 2000; 1: 191–198. - PubMed
-
- Martinsen EW. Benefits of exercise for the treatment of depression. Sports Med 1990; 9: 380–389. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

