Lamivudine/Adefovir Treatment Increases the Rate of Spontaneous Mutation of Hepatitis B Virus in Patients
- PMID: 27649318
- PMCID: PMC5029863
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163363
Lamivudine/Adefovir Treatment Increases the Rate of Spontaneous Mutation of Hepatitis B Virus in Patients
Abstract
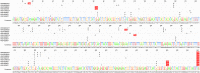
The high levels of genetic diversity shown by hepatitis B virus (HBV) are commonly attributed to the low fidelity of its polymerase. However, the rate of spontaneous mutation of human HBV in vivo is currently unknown. Here, based on the evolutionary principle that the population frequency of lethal mutations equals the rate at which they are produced, we have estimated the mutation rate of HBV in vivo by scoring premature stop codons in 621 publicly available, full-length, molecular clone sequences derived from patients. This yielded an estimate of 8.7 × 10-5 spontaneous mutations per nucleotide per cell infection in untreated patients, which should be taken as an upper limit estimate because PCR errors and/or lack of effective lethality may inflate observed mutation frequencies. We found that, in patients undergoing lamivudine/adefovir treatment, the HBV mutation rate was elevated by more than sixfold, revealing a mutagenic effect of this treatment. Genome-wide analysis of single-nucleotide polymorphisms indicated that lamivudine/adefovir treatment increases the fraction of A/T-to-G/C base substitutions, consistent with recent work showing similar effects of lamivudine in cellular DNA. Based on these data, the rate at which HBV produces new genetic variants in treated patients is similar to or even higher than in RNA viruses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase sequence variant database for sequence analysis and mutation discovery.Antiviral Res. 2010 Dec;88(3):269-75. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2010.09.012. Epub 2010 Sep 25. Antiviral Res. 2010. PMID: 20875460 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibility of hepatitis B virus to lamivudine restored by resistance to adefovir.J Med Virol. 2009 Mar;81(3):413-6. doi: 10.1002/jmv.21401. J Med Virol. 2009. PMID: 19152408
-
Clinical course and predictive factors of virological response in long-term lamivudine plus adefovir dipivoxil combination therapy for lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B patients.J Med Virol. 2011 Jun;83(6):953-61. doi: 10.1002/jmv.22025. J Med Virol. 2011. PMID: 21503906
-
Adefovir dipivoxil in chronic hepatitis B infection.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2004 Nov;5(11):2361-7. doi: 10.1517/14656566.5.11.2361. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2004. PMID: 15500383 Review.
-
[Therapy for chronic hepatitis B: relationship between HBV genotype and efficacy or resistance of anti-viral therapy].Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2007 Oct;104(10):1459-64. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2007. PMID: 17917393 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Estimating hepatitis B virus cccDNA persistence in chronic infection.Virus Evol. 2020 Aug 25;7(1):veaa063. doi: 10.1093/ve/veaa063. eCollection 2021 Jan. Virus Evol. 2020. PMID: 33732502 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

