Identification of Claudin 1 Transcript Variants in Human Invasive Breast Cancer
- PMID: 27649506
- PMCID: PMC5029943
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163387
Identification of Claudin 1 Transcript Variants in Human Invasive Breast Cancer
Abstract
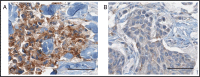
Background: The claudin 1 tight junction protein, solely responsible for the barrier function of epithelial cells, is frequently down regulated in invasive human breast cancer. The underlying mechanism is largely unknown, and no obvious mutations in the claudin 1 gene (CLDN1) have been identified to date in breast cancer. Since many genes have been shown to undergo deregulation through splicing and mis-splicing events in cancer, the current study was undertaken to investigate the occurrence of transcript variants for CLDN1 in human invasive breast cancer.
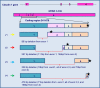
Methods: RT-PCR analysis of CLDN1 transcripts was conducted on RNA isolated from 12 human invasive breast tumors. The PCR products from each tumor were resolved by agarose gel electrophoresis, cloned and sequenced. Genomic DNA was also isolated from each of the 12 tumors and amplified using PCR CLDN1 specific primers. Sanger sequencing and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analyses were conducted.
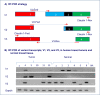
Results: A number of CLDN1 transcript variants were identified in these breast tumors. All variants were shorter than the classical CLDN1 transcript. Sequence analysis of the PCR products revealed several splice variants, primarily in exon 1 of CLDN1; resulting in truncated proteins. One variant, V1, resulted in a premature stop codon and thus likely led to nonsense mediated decay. Interestingly, another transcript variant, V2, was not detected in normal breast tissue samples. Further, sequence analysis of the tumor genomic DNA revealed SNPs in 3 of the 4 coding exons, including a rare missense SNP (rs140846629) in exon 2 which represents an Ala124Thr substitution. To our knowledge this is the first report of CLDN1 transcript variants in human invasive breast cancer. These studies suggest that alternate splicing may also be a mechanism by which claudin 1 is down regulated at both the mRNA and protein levels in invasive breast cancer and may provide novel insights into how CLDN1 is reduced or silenced in human breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exists.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson JM (2001) Molecular structure of tight junctions and their role in epithelial transport. News Physiol Sci 16: 126–130. - PubMed
-
- Balda MS, Matter K (1998) Tight junctions. J Cell Sci 111: 541–547. - PubMed
-
- Balda MS, Whitney JA, Flores C, Gonzalez S, Cereijido M, Matter K (1996) Functional dissociation of paracellular permeability and transepithelial electrical resistance and disruption of the apical-basolateral intramembrane diffusion barrier by expression of a mutant tight junction membrane protein. JCell Biol 134: 1031–1049. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

