Epac2-Rap1 Signaling Regulates Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Susceptibility to Cardiac Arrhythmias
- PMID: 27649969
- PMCID: PMC5510674
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2015.6485
Epac2-Rap1 Signaling Regulates Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Susceptibility to Cardiac Arrhythmias
Abstract
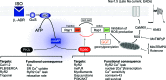
Aims: In the heart, β1-adrenergic signaling involves cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) acting via both protein kinase-A (PKA) and exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (Epac): a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for the small GTPase Rap1. Inhibition of Epac-Rap1 signaling has been proposed as a therapeutic strategy for both cancer and cardiovascular disease. However, previous work suggests that impaired Rap1 signaling may have detrimental effects on cardiac function. The aim of the present study was to investigate the influence of Epac2-Rap1 signaling on the heart using both in vivo and in vitro approaches.
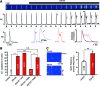
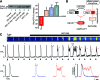
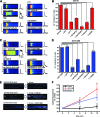
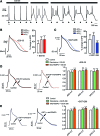
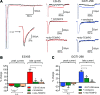
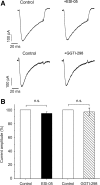
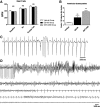
Results: Inhibition of Epac2 signaling induced early afterdepolarization arrhythmias in ventricular myocytes. The underlying mechanism involved an increase in mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and activation of the late sodium current (INalate). Arrhythmias were blocked by inhibition of INalate or the mitochondria-targeted antioxidant, mitoTEMPO. In vivo, inhibition of Epac2 caused ventricular tachycardia, torsades de pointes, and sudden death. The in vitro and in vivo effects of Epac2 inhibition were mimicked by inhibition of geranylgeranyltransferase-1, which blocks interaction of Rap1 with downstream targets.
Innovation: Our findings show for the first time that Rap1 acts as a negative regulator of mitochondrial ROS production in the heart and that impaired Epac2-Rap1 signaling causes arrhythmias due to ROS-dependent activation of INalate. This has implications for the use of chemotherapeutics that target Epac2-Rap1 signaling. However, selective inhibition of INalate provides a promising strategy to prevent arrhythmias caused by impaired Epac2-Rap1 signaling.
Conclusion: Epac2-Rap1 signaling attenuates mitochondrial ROS production and reduces myocardial arrhythmia susceptibility. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 27, 117-132.
Keywords: Ca2+; Epac; ROS; Rap1; arrhythmias; cardiac.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
cAMP-Epac2-mediated activation of Rap1 in developing male germ cells: RA-RhoGAP as a possible direct down-stream effector.Mol Reprod Dev. 2009 Apr;76(4):407-16. doi: 10.1002/mrd.20963. Mol Reprod Dev. 2009. PMID: 18937323
-
EPAC activation inhibits acetaldehyde-induced activation and proliferation of hepatic stellate cell via Rap1.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016 May;94(5):498-507. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2015-0437. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26854595
-
Novel Epac fluorescent ligand reveals distinct Epac1 vs. Epac2 distribution and function in cardiomyocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Mar 31;112(13):3991-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1416163112. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25829540 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory actions of 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate on osteoclast function: possible roles of Epac-mediated signaling.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018 Dec;1433(1):18-28. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13861. Epub 2018 May 30. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018. PMID: 29846007 Review.
-
Epac2-dependent rap1 activation and the control of islet insulin secretion by glucagon-like peptide-1.Vitam Horm. 2010;84:279-302. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-381517-0.00010-2. Vitam Horm. 2010. PMID: 21094904 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spatial Mechano-Signaling Regulation of GTPases through Non-Degradative Ubiquitination.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Dec;10(36):e2303367. doi: 10.1002/advs.202303367. Epub 2023 Nov 9. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37946677 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the mitochondrial nuclease EndoG in the regulation of cell proliferation through the control of reactive oxygen species.Redox Biol. 2020 Oct;37:101736. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101736. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 33032073 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell sequencing combined with machine learning reveals the mechanism of interaction between epilepsy and stress cardiomyopathy.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 27;14:1078731. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1078731. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36776884 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulating miR-184 relieves calcium oxalate crystal-mediated renal cell damage via activating the Rap1 signaling pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Dec 27;15(24):14749-14763. doi: 10.18632/aging.205286. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 38154105 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin-(1-7) Attenuates Protein O-GlcNAcylation in the Retina by EPAC/Rap1-Dependent Inhibition of O-GlcNAc Transferase.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 Feb 7;61(2):24. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.2.24. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32068794 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
