Telocytes in pancreas of the Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus)
- PMID: 27650046
- PMCID: PMC5082396
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12948
Telocytes in pancreas of the Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus)
Abstract
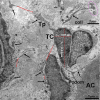
Telocytes (TCs), novel interstitial cells, have been identified in various organs of many mammals. However, information about TCs of lower animals remains rare. Herein, pancreatic TCs of the Chinese giant salamanders (Andrias davidianus) were identified by CD34 immunohistochemistry (IHC) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The IHC micrographs revealed CD34+ TCs with long telopodes (Tps) that were located in the interstitium of the pancreas. CD34+ TCs/Tps were frequently observed between exocrine acinar cells and were close to blood vessels. The TEM micrographs also showed the existence of TCs in the interstitium of the pancreas. TCs had distinctive ultrastructural features, such as one to three very long and thin Tps with podoms and podomers, caveolae, dichotomous branching, neighbouring exosomes and vesicles. The Tps and exosomes were found in close proximity to exocrine acinar cells and α cells. It is suggested that TCs may play a role in the regeneration of acinar cells and α cells. In conclusion, our results demonstrated the presence of TCs in the pancreas of the Chinese giant salamander. This finding will assist us in a better understanding of TCs functions in the amphibian pancreas.
Keywords: amphibian; pancreas; telocytes; ultrastructure.
© 2016 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Telocytes in gastric lamina propria of the Chinese giant salamander, Andrias davidianus.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 15;6:33554. doi: 10.1038/srep33554. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27629815 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrastructure of telocytes, a new type of interstitial cells in the myocardium of the Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus).Eur J Histochem. 2019 May 23;63(2):3021. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2019.3021. Eur J Histochem. 2019. PMID: 31122004 Free PMC article.
-
Telocytes in ileum of the Chinese giant salamander: ultrastructural evidence.J Cell Mol Med. 2016 Mar;20(3):568-74. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12741. Epub 2016 Jan 25. J Cell Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 26805522 Free PMC article.
-
The Cutaneous Telocytes.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;913:303-323. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-1061-3_20. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27796896 Review.
-
Telocytes in skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle interstitium: morphological and functional aspects.Histol Histopathol. 2018 Nov;33(11):1151-1165. doi: 10.14670/HH-11-994. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Histol Histopathol. 2018. PMID: 29693711 Review.
Cited by
-
Cultured Chinese Giant Salamander Skin and Skin Secretions as a Source of Bioactive Peptides for Food and Medicine.Food Sci Anim Resour. 2025 Jan;45(1):109-125. doi: 10.5851/kosfa.2024.e114. Epub 2025 Jan 1. Food Sci Anim Resour. 2025. PMID: 39840243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac Telocytes 16 Years on-What Have We Learned So Far, and How Close Are We to Routine Application of the Knowledge in Cardiovascular Regenerative Medicine?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 10;22(20):10942. doi: 10.3390/ijms222010942. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Telocytes in the Pancreas of Turtles-A role in Cellular Communication.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 17;21(6):2057. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062057. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32192184 Free PMC article.
-
Telocytes enhanced the proliferation, adhesion and motility of endometrial stromal cells as mediated by the ERK pathway in vitro.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Feb 15;11(2):572-585. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 30899363 Free PMC article.
-
Telocytes and Their Structural Relationships With the Sperm Storage Tube and Surrounding Cell Types in the Utero-Vaginal Junction of the Chicken.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Mar 24;9:852407. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.852407. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35400114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Popescu LM. The Tandem: telocytes – stem cells. Int J Biol Biomed Eng. 2011; 5: 83–92.
-
- Cretoiu SM, Popescu LM. Telocytes revisited. Biomol Concepts. 2014; 5: 353–69. - PubMed
-
- Cretoiu D, Cretoiu SM, Simionescu AA, et al Telocytes, a distinct type of cell among the stromal cells present in the lamina propria of jejunum. Histol Histopathol. 2012; 27: 1067–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

