The Influence of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor and Bone Morphogenetic Protein Presentation on Tubule Organization by Human Umbilical Vascular Endothelial Cells and Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Coculture
- PMID: 27650131
- PMCID: PMC5107722
- DOI: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2016.0163
The Influence of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor and Bone Morphogenetic Protein Presentation on Tubule Organization by Human Umbilical Vascular Endothelial Cells and Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Coculture
Abstract
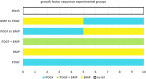
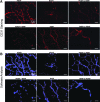
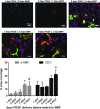
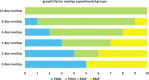
A three-dimensional in vitro Matrigel plug was used as a model to explore delivery patterns of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) to a coculture of human mesenchymal and endothelial cells. While BMP-2 is well recognized for its role in promoting fracture healing through proliferation and differentiation of osteoclast precursors, it is not a growth factor known to promote the process of angiogenesis, which is also critical for complete bone tissue repair. PDGF, in contrast, is a known regulator of angiogenesis, and also a powerful chemoattractant for osteoblast precursor cells. It has been suggested that presentation of PDGF followed by BMP may better promote vascularized bone tissue formation. Yet, it is unclear as to how cells would respond to various durations of delivery of each growth factor as well as to various amounts of overlap in presentation in terms of angiogenesis. Using a three-dimensional in vitro Matrigel plug model, we observed how various presentation schedules of PDGF and BMP-2 influenced tubule formation by human mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vascular endothelial cells. We observed that sequential presentation of PDGF to BMP-2 led to increased tubule formation over simultaneous delivery of these growth factors. Importantly, a 2-4 day overlap in the sequential presentation of PDGF and BMP-2 increased tubule formation as compared with groups with zero or complete growth factor overlap, suggesting that a moderate amount of angiogenic and osteogenic growth factor overlap may be beneficial for processes associated with angiogenesis.
Keywords: 3D cell culture; angiogenesis; endothelial cells; growth factors; mesenchymal stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Statement No competing financial interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
* Programmed Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB and Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Delivery from a Hybrid Calcium Phosphate/Alginate Scaffold.Tissue Eng Part A. 2017 Dec;23(23-24):1382-1393. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2017.0027. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017. PMID: 28537482 Free PMC article.
-
Efficiency of coculture with angiogenic cells or physiological BMP-2 administration on improving osteogenic differentiation and bone formation of MSCs.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019 Mar;107(3):643-653. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.36581. Epub 2018 Dec 5. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019. PMID: 30458064
-
BMPER Enhances Bone Formation by Promoting the Osteogenesis-Angiogenesis Coupling Process in Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;45(5):1927-1939. doi: 10.1159/000487969. Epub 2018 Mar 2. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29518774
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 9 enhances osteogenic and angiogenic responses of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells cocultured with umbilical vein endothelial cells through the PI3K/AKT/m-TOR signaling pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Nov 27;13(22):24829-24849. doi: 10.18632/aging.203718. Epub 2021 Nov 27. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34837694 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-derived growth factor receptors regulate mesenchymal stem cell fate: implications for neovascularization.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2010 Jan;10(1):57-71. doi: 10.1517/14712590903379510. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20078229 Review.
Cited by
-
Transgenic PDGF-BB sericin hydrogel potentiates bone regeneration of BMP9-stimulated mesenchymal stem cells through a crosstalk of the Smad-STAT pathways.Regen Biomater. 2022 Nov 30;10:rbac095. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbac095. eCollection 2023. Regen Biomater. 2022. PMID: 36683747 Free PMC article.
-
[Basic principles of fracture healing].Orthopade. 2017 Aug;46(8):640-647. doi: 10.1007/s00132-017-3449-8. Orthopade. 2017. PMID: 28718007 Review. German.
-
Hyaluronic Acid Promotes the Osteogenesis of BMP-2 in an Absorbable Collagen Sponge.Polymers (Basel). 2017 Aug 4;9(8):339. doi: 10.3390/polym9080339. Polymers (Basel). 2017. PMID: 30971019 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review and advanced biomolecule-based therapies for osteoporosis.J Adv Res. 2025 May;71:337-354. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.05.024. Epub 2024 May 27. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 38810908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E3 ligase HUWE1 promotes PDGF D-mediated osteoblastic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by effecting polyubiquitination of β-PDGFR.J Biol Chem. 2022 Jun;298(6):101981. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101981. Epub 2022 Apr 25. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35472332 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Megas P., and Panagiotis M. Classification of non-union. Injury 36 Suppl 4, S30, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Toolan B., and Sangeozan B. Fractures of the talus: anatomy, evaluation, and management. Medscape General Medicine 1, 1999
-
- Butler M., Forte M., and Kane R. Treatment of Common Hip Fractures. Rockville, MD, US: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Borrelli J., Prickett W., Song E., Becker D., and Ricci W. Extraosseous blood supply of the tibia and the effects of different plating techniques: a human cadaveric study. J Orthop Trauma 16, 691, 2002 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

