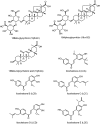
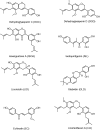
The anti-inflammatory activity of licorice, a widely used Chinese herb
- PMID: 27650551
- PMCID: PMC7012004
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2016.1225775
The anti-inflammatory activity of licorice, a widely used Chinese herb
Abstract
Context: Increasing incidence and impact of inflammatory diseases have encouraged the search of new pharmacological strategies to face them. Licorice has been used to treat inflammatory diseases since ancient times in China.
Objective: To summarize the current knowledge on anti-inflammatory properties and mechanisms of compounds isolated from licorice, to introduce the traditional use, modern clinical trials and officially approved drugs, to evaluate the safety and to obtain new insights for further research of licorice.
Methods: PubMed, Web of Science, Science Direct and ResearchGate were information sources for the search terms 'licorice', 'licorice metabolites', 'anti-inflammatory', 'triterpenoids', 'flavonoids' and their combinations, mainly from year 2010 to 2016 without language restriction. Studies were selected from Science Citation Index journals, in vitro studies with Jadad score less than 2 points and in vivo and clinical studies with experimental flaws were excluded.
Results: Two hundred and ninety-five papers were searched and 93 papers were reviewed. Licorice extract, 3 triterpenes and 13 flavonoids exhibit evident anti-inflammatory properties mainly by decreasing TNF, MMPs, PGE2 and free radicals, which also explained its traditional applications in stimulating digestive system functions, eliminating phlegm, relieving coughing, nourishing qi and alleviating pain in TCM. Five hundred and fifty-four drugs containing licorice have been approved by CFDA. The side effect may due to the cortical hormone like action.
Conclusion: Licorice and its natural compounds have demonstrated anti-inflammatory activities. More pharmacokinetic studies using different models with different dosages should be carried out, and the maximum tolerated dose is also critical for clinical use of licorice extract and purified compounds.
Keywords: Glycyrrhiza glabra L.; Glycyrrhiza inflata Bat.; Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch.; flavonoid; glycyrrhetinic acid; glycyrrhizin.
Figures
References
-
- Ahn SJ, Cho EJ, Kim HJ, Park SN, Lim YK, Kook JK.. 2012. The antimicrobial effects of deglycyrrhizinated licorice root extract on Streptococcus mutans UA159 in both planktonic and biofilm cultures. Anaerobe. 18:590–596. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharjee S, Bhattacharjee A, Majumder S, Majumdar SB, Majumdar S.. 2012. . Glycyrrhizic acid suppresses Cox-2-mediated anti-inflammatory responses during Leishmania donovani infection . J Antimicrob Chemother. 67:1905–1914. - PubMed
-
- Bi X, Gong M, Di L.. 2014. Review on prescription compatibility of shaoyaogancao decoction and reflection on pharmacokinetic compatibility mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine prescription based on in vivo drug interaction of main efficacious compounds. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014:208129. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carrasco-Pozo C, Castillo RL, Beltrán C, Miranda A, Fuentes J, Gotteland M.. 2016. Molecular mechanisms of gastrointestinal protection by quercetin against indomethacin-induced damage: role of NF-κB and Nrf2. J Nutr Biochem. 27:289–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources