Ten Years of Preserved Kidney Function After Islet Transplant Graft Failure
- PMID: 27650978
- PMCID: PMC5127237
- DOI: 10.2337/dc16-1093
Ten Years of Preserved Kidney Function After Islet Transplant Graft Failure
Figures
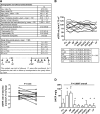
References
-
- Fiorina P, Folli F, Zerbini G, et al. . Islet transplantation is associated with improvement of renal function among uremic patients with type I diabetes mellitus and kidney transplants. J Am Soc Nephrol 2003;14:2150–2158 - PubMed
-
- Shapiro AM. Islet transplants and impact on secondary diabetic complications: does C-Peptide protect the kidney? J Am Soc Nephrol 2003;14:2214–2216 - PubMed
-
- Thompson DM, Meloche M, Ao Z, et al. . Reduced progression of diabetic microvascular complications with islet cell transplantation compared with intensive medical therapy. Transplantation 2011;91:373–378 - PubMed
-
- Maffi P, Bertuzzi F, De Taddeo F, et al. . Kidney function after islet transplant alone in type 1 diabetes: impact of immunosuppressive therapy on progression of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Care 2007;30:1150–1155 - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

