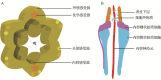[The effect of glial cells in the function and development of the nervous system in Caenorhabditis elegans]
- PMID: 27651199
- PMCID: PMC10396986
- DOI: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2016.05.16
[The effect of glial cells in the function and development of the nervous system in Caenorhabditis elegans]
Abstract
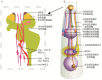
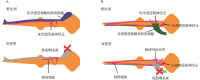
There are three types of glial cells in Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans for short): sheath glia, socket glia and glutamate receptor glia. They are mainly located in four sensory organs including the amphid, the cephalic organ, the outer labial sensilla and the inner labial sensilla. C. elegans glial cells play key roles in dendrite extension, neurite guidance and extension, and are essential for synaptogenesis and maintain the normal morphology and the function of sensory nerve endings as well. A recent study shown that some nematode neurons are derived from the glial cells. Moreover, nematodes glial cells can directly modulate the function of sensory neurons. Some glial cells can also respond to certain external stimuli, such as mechanical stimulation, and adjust the accompanying neuronal activities.The article summarizes the progress on effects of nematodes glial cells on the nervous system development and function.
秀丽隐杆线虫(简称线虫)神经胶质细胞(简称胶质细胞)分为三种类型:鞘状胶质细胞、槽状胶质细胞和谷氨酸受体胶质细胞,主要分布在化学感受器、头部感受器、外唇感受器和内唇感受器这四种感觉器官中。在神经系统发育过程中,胶质细胞在线虫神经元的树突延伸和轴突的导向延伸中发挥关键作用,还参与了突触生成,并且通过形成感受器通道的方式来维持感觉神经末梢的正常形态和功能。此外,线虫胶质细胞还可作为神经元的起源。在神经系统成熟过程中,线虫胶质细胞既可通过维持神经元形态来间接控制感觉神经元的功能,也可直接控制感觉神经元的功能。有些胶质细胞可以感受特定的外界刺激,用这些信息来调节与之相伴神经元的活动。线虫胶质细胞不仅通过神经元来影响神经系统,其自身也可以感受机械刺激。本文总结了目前已知线虫胶质细胞对神经发育和功能影响的研究进展。
Similar articles
-
Cell-type-specific promoters for C. elegans glia.J Neurogenet. 2020 Sep-Dec;34(3-4):335-346. doi: 10.1080/01677063.2020.1781851. Epub 2020 Jul 22. J Neurogenet. 2020. PMID: 32696701 Free PMC article.
-
Glia actively sculpt sensory neurons by controlled phagocytosis to tune animal behavior.Elife. 2021 Mar 24;10:e63532. doi: 10.7554/eLife.63532. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33759761 Free PMC article.
-
Dye-filling of the amphid sheath glia: implications for the functional relationship between sensory neurons and glia in Caenorhabditis elegans.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Mar 11;406(2):188-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.02.003. Epub 2011 Feb 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011. PMID: 21295547
-
Glial development and function in the nervous system of Caenorhabditis elegans.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 Jan 8;7(4):a020578. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a020578. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015. PMID: 25573712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The glia of Caenorhabditis elegans.Glia. 2011 Sep;59(9):1253-63. doi: 10.1002/glia.21084. Epub 2010 Nov 2. Glia. 2011. PMID: 21732423 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- BARRES B A. The mystery and magic of glia: a perspective on their roles in health and disease. Neuron. 2008;60(3):430–440. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.10.013. [BARRES B A. The mystery and magic of glia: a perspective on their roles in health and disease[J]. Neuron, 2008, 60(3): 430-440.] - DOI - PubMed
-
- ZHANG Y, LU H, BARGMANN C I. Pathogenic bacteria induce aversive olfactory learning in Caenorhabditis elegans . Nature. 2005;438(7065):179–184. doi: 10.1038/nature04216. [ZHANG Y, LU H, BARGMANN C I. Pathogenic bacteria induce aversive olfactory learning in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Nature, 2005, 438(7065): 179-184. ] - DOI - PubMed
-
- BACAJ T, TEVLIN M, LU Y, et al. Glia are essential for sensory organ function in C. elegans . Science. 2008;322(5902):744–747. doi: 10.1126/science.1163074. [BACAJ T, TEVLIN M, LU Y, et al. Glia are essential for sensory organ function in C. elegans[J]. Science, 2008, 322(5902): 744-747. ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- BARGMANN C I. Chemosensation in C. elegans . http://dev.wormbook.org/chapters/www_chemosensation/chemosensation.pdf. WormBook. 2006:1–29. [BARGMANN C I. Chemosensation in C. elegans[J]. WormBook, 2006: 1-29. ] - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources