Comparison Between Sublingual and Vaginal Administration of Misoprostol in Management of Missed Abortion
- PMID: 27651573
- PMCID: PMC5016400
- DOI: 10.1007/s13224-015-0757-y
Comparison Between Sublingual and Vaginal Administration of Misoprostol in Management of Missed Abortion
Abstract
Aim: The aim of the present study is to compare between sublingual administration of misoprostol and vaginal administration in the management of missed abortion.
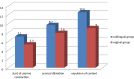
Materials and methods: The study was conducted in El-Shatby Maternity Hospital on 160 patients diagnosed as missed abortion by ultrasonographic examination. Cases were divided into two groups according to the methods of misoprostol administration, whether sublingual or vaginal. Patients of the two groups were observed for the times of uterine colic starting, cervical dilation, and conceptus expulsion, along with recording of any side effects.
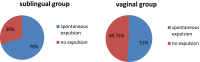
Result: During the follow-up of our cases we found that sublingual route is more effective than vaginal route in the management of missed abortion. The difference between the two groups in percentage of conceptus expulsion was statistically significant. The most common side effects were nausea which was present in 55 % of cases in group I (sublingual) and in 40 % of cases in group II (vaginal) then severe pain in 25 % of cases in group I (sublingual) and in 20 % of cases in group II (vaginal) and hyperpyrexia in 15 % of cases in group I (sublingual) and in 5 % of cases in group II (vaginal).
Conclusion: Sublingual administration of misoprostol is more effective than its vaginal administration in missed abortion management. Side effect of misoprostol as nausea, vomiting, fever is more common with sublingual administration in comparison with its vaginal administration.
Keywords: Abortion; Misoprostol; Sublingual; Vaginal.
Conflict of interest statement
None. Ethical approval It meets ethical guidelines as the manuscript has been approved by ethics committee of Alexandria medical school, and a written consent has been taken from all patients about participation in research.
Figures
References
-
- Alberma E, Grudzinskas G, Chardt G. Spontaneous abortion: diagnosis and treatment. London: Springer; 1992. pp. 9–20.
-
- Schorge JO, Schaffer JI, Halvorson LM, et al. First-trimester abortion. In: Schorge JO, Schaffer JI, et al., editors. Williams Gynecology. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources