Role of l-Arginine in Oligohydramnios
- PMID: 27651617
- PMCID: PMC5016450
- DOI: 10.1007/s13224-016-0853-7
Role of l-Arginine in Oligohydramnios
Abstract
Background: Oligohydramnios is a known obstetric complication which is associated with operative interferences and perinatal morbidity and mortality. l-arginine is a precursor of nitric oxide and may play a role in local vasodilatation. Administration of l-arginine has been suggested to improve amniotic fluid index (AFI) in oligohydramnios.
Aims and objectives: To study the effect of l-arginine in optimizing fetal outcome in cases of oligohydramnios.
Materials and methods: A retrospective study was conducted at Dr L H Hiranandani hospital consisting of 100 antenatal patients diagnosed with oligohydramnios [AFI < 8 cm] remote from term. Patients were evaluated for all antenatal risk factors and were started on l-arginine sachets (3 g, 3 sachets a day). The treatment was continued till an adequate improvement in liquor was noted. However, patients were considered for delivery if the liquor remained <5. Further, mean increase in AFI, intervention delivery interval, and neonatal outcome were studied.
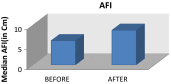
Results: The mean gestational age at the time of recruitment was 32.3 weeks. The mean AFI noted was 5.421 cm. These patients were delivered at 35 ± 1.1 weeks, and thus, pregnancy could be prolonged by 2.4 ± 1.1 weeks. The mean AFI at the end of therapeutic intervention was 8.753, and thus, an AFI increase of 3.332 cm could be obtained. There was no significant neonatal morbidity in these patients. Significant improvement in liquor volume was obtained in these patients after intervention with l-arginine sachets.
Conclusion: l-arginine supplementation is promising in improving volume of amniotic fluid in cases of oligohydramnios and prolonging pregnancy by a mean of 2.4 weeks, allowing fetal lung maturation thus benefiting the neonatal outcome.
Keywords: Amniotic fluid index; Oligohydramnios; l-arginine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest. Ethical Approval This study is approved by the institutional scientific and ethical committee. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed Consent Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Similar articles
-
Serial assessment of amniotic fluid index in uncomplicated term pregnancies: prognostic value of amniotic fluid reduction.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2004 Apr;15(4):233-6. doi: 10.1080/14767050410001668671. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2004. PMID: 15280130
-
Perinatal outcome associated with oligohydramnios in uncomplicated term pregnancies.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2004 Jan;269(2):130-3. doi: 10.1007/s00404-003-0525-6. Epub 2003 Aug 20. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2004. PMID: 12928935
-
Intravenous maternal hydration in third trimester oligohydramnios: effect on amniotic fluid volume.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2007 Jun;17(6):336-9. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2007. PMID: 17623581
-
The role of amniotic fluid assessment in indicated preterm delivery.Semin Perinatol. 2011 Oct;35(5):286-91. doi: 10.1053/j.semperi.2011.05.012. Semin Perinatol. 2011. PMID: 21962628 Review.
-
The evidence for abandoning the amniotic fluid index in favor of the single deepest pocket.Am J Perinatol. 2007 Oct;24(9):549-55. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-986689. Epub 2007 Oct 1. Am J Perinatol. 2007. PMID: 17909990 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Amino Acid Infusion on Amniotic Fluid Index in Pregnancies Associated With Oligohydramnios and Fetal Growth Restriction.Cureus. 2023 May 15;15(5):e39027. doi: 10.7759/cureus.39027. eCollection 2023 May. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37378206 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of maternal intravenous hydration on amniotic fluid index in oligohydramnios.BMC Res Notes. 2022 Mar 7;15(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s13104-022-05985-6. BMC Res Notes. 2022. PMID: 35255952 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of L-Arginine in Pregnancy and Beyond: An Emerging Pharmacogenomic Approach.Curr Gene Ther. 2025;25(1):22-33. doi: 10.2174/0115665232262213240329034826. Curr Gene Ther. 2025. PMID: 38644716 Review.
References
-
- Zhang N, Xiong AH, Xiao X, et al. Effect and mechanism of l-arginine therapy for fetal growth retardation due to pregnancy-induced hypertension. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2007;27(2):198–200. - PubMed
-
- Appleton J. Arginine: clinical potential of a semi essential amino acid. Altern Med Rev. 2002;7:512–522. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources