Formulation and in vitro evaluation of a fast-disintegrating/sustained dual release bucoadhesive bilayer tablet of captopril for treatment of hypertension crises
- PMID: 27651807
- PMCID: PMC5022375
- DOI: 10.4103/1735-5362.189284
Formulation and in vitro evaluation of a fast-disintegrating/sustained dual release bucoadhesive bilayer tablet of captopril for treatment of hypertension crises
Abstract
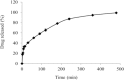
Hypertension crisis is one of the main health problems and its effective treatment is of high importance. For this purpose, fast-disintegrating and sustained release formulations of captopril, as a drug of choice, were prepared using conventional mucoadhesive polymers hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (Na-CMC), hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC), Carbopol 934 (CP934) and sodium alginate (Na-alg). The optimum sustained release formulations were selected based on mean dissolution time (MDT). The swellability and mucoadhesive properties of selected formulations were assessed and compared. A direct relationship between swelling and release rates/adhesiveness of sustained release formulations was observed. The results showed that formulations containing combination of CP934 and cellulose-based polymers had the highest swellability, sustainability and adhesion strength. These formulations prolonged drug release up to 8 h showing good fitness to Korsemeyer-Peppas model. Moreover, the adopted fast-disintegrating tablet could release up to 100% of drug within 3 min in oral pH. Finally, a dual fast-disintegrating/sustained release bucoadhesive bilayer tablet consisting of optimized formulations was prepared releasing 30% of the drug initially within 15 min and the remaining up to 8 h which could be considered as an appropriate formulation for the treatment of hypertension crises.
Keywords: Bilayer; Bucoadhesive; Captopril; Dual release; Fast-disintegrating; Sustained release.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Formulation and Evaluation of Cefixime Trihydrate Matrix Tablets Using HPMC, Sodium CMC, Ethyl Cellulose.Indian J Pharm Sci. 2015 May-Jun;77(3):321-7. doi: 10.4103/0250-474x.159663. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2015. PMID: 26180278 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation of nicotine mucoadhesive tablet for smoking cessation and evaluation of its pharmaceuticals properties.Adv Biomed Res. 2013 Nov 30;2:88. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.122515. eCollection 2013. Adv Biomed Res. 2013. PMID: 24524034 Free PMC article.
-
Design and In Vitro/In Vivo Evaluation of Ultra-Thin Mucoadhesive Buccal Film Containing Fluticasone Propionate.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2017 Jan 1;18(1):93-103. doi: 10.1208/s12249-016-0496-0. Epub 2016 Feb 16. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2017. PMID: 26883262
-
Development and characterization of gastroretentive sustained-release formulation by combination of swelling and mucoadhesive approach: a mechanistic study.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2013 Dec 5;7:1455-69. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S52890. eCollection 2013. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2013. PMID: 24348022 Free PMC article.
-
Neuro-fuzzy modeling of ibuprofen-sustained release from tablets based on different cellulose derivatives.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2019 Feb;9(1):162-177. doi: 10.1007/s13346-018-00592-0. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 30341764
Cited by
-
The Impact of Hypromellose on Pharmaceutical Properties of Alginate Microparticles as Novel Drug Carriers for Posaconazole.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 28;24(13):10793. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310793. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445975 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication, optimization and characterization of an osmotic push-pull drug delivery system for paliperidone.J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2023 Aug 30;18(6):1511-1518. doi: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2023.08.002. eCollection 2023 Dec. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37693824 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of two types of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors on the hypertension induced by new pressor protein associated with beta-factor XIIa in rats.Res Pharm Sci. 2020 May 11;15(2):174-181. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.283817. eCollection 2020 Apr. Res Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 32582357 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Omidian H, Park K. Oral targeted drug delivery systems: gastric retention devices. In: Wen H, Park K, editors. Oral controlled release formulation design and drug delivery: Theory to practice. New Jersey: Wiley; 2010. pp. 185–204.
-
- Davis SS. Formulation strategies for absorption windows. Drug Discov Today. 2005;10(4):249–257. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman A, Stepensky D, Lavy E, Eyal S, Klausner E, Friedman M. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic aspects of gastroretentive dosage forms. Int J Pharm. 2004;277:141–153. - PubMed
-
- Sweetman SC, editor. Martindale the complete drug reference. 36 ed. London, Chicago: Pharmaceutical Press; 2009. Cardiovascular Drugs, Captopril; pp. 1239–1240.
-
- Gabor F, Fillafer C, Neutsch L, Ratzinger G, Wirth M. Improving oral delivery. In: Schäfer-Kortin M, editor. Drug delivery. Berlin: Springer; 2010. pp. 345–398. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
