Asymmetric division: An antitumor player?
- PMID: 27652318
- PMCID: PMC4972103
- DOI: 10.1080/23723556.2016.1164279
Asymmetric division: An antitumor player?
Abstract
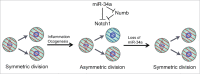
miR-34a-mediated asymmetric cell division reins in excessive stem cell expansion during tissue regeneration in the intestine and colon. Loss of miR-34a switches asymmetric division to symmetric division and enhances stem cell proliferation. Asymmetric division also occurs in the early stages of colon cancer stem cells. Mechanistically, miR-34a, Numb, and Notch form a feed-forward loop that specifies cell fate when stem cells divide.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A miR-34a-Numb Feedforward Loop Triggered by Inflammation Regulates Asymmetric Stem Cell Division in Intestine and Colon Cancer.Cell Stem Cell. 2016 Feb 4;18(2):189-202. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.01.006. Cell Stem Cell. 2016. PMID: 26849305 Free PMC article.
-
Myogenic cells fates are antagonized by Notch only in asymmetric lineages of the Drosophila heart, with or without cell division.Development. 2003 Jul;130(13):3039-51. doi: 10.1242/dev.00484. Development. 2003. PMID: 12756185
-
Gαs regulates asymmetric cell division of cortical progenitors by controlling Numb mediated Notch signaling suppression.Neurosci Lett. 2015 Jun 15;597:97-103. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.04.034. Epub 2015 Apr 24. Neurosci Lett. 2015. PMID: 25916881
-
The asymmetric division and tumorigenesis of stem cells.Chin J Cancer. 2010 Mar;29(3):248-53. doi: 10.5732/cjc.009.10668. Chin J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20193105 Review.
-
Asymmetric cell division of stem cells in the lung and other systems.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Jul 31;2:33. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2014.00033. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 25364740 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evodiamine Eliminates Colon Cancer Stem Cells via Suppressing Notch and Wnt Signaling.Molecules. 2019 Dec 10;24(24):4520. doi: 10.3390/molecules24244520. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31835579 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Notch pathway components (Numb, Itch, and Siah-1) in colorectal tumors: A clinicopathological study.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Jul 14;26(26):3814-3833. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i26.3814. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32774060 Free PMC article.
-
Deregulation of cancer-stem-cell-associated miRNAs in tissues and sera of colorectal cancer patients.Oncotarget. 2020 Jan 14;11(2):116-130. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27411. eCollection 2020 Jan 14. Oncotarget. 2020. PMID: 32010426 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clevers H. Stem cells, asymmetric division and cancer. Nat Genet 2005; 37:1027-8; PMID:16195718; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ng1005-1027 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Snippert HJ, van der Flier LG, Sato T, van Es JH, van den Born M, Kroon-Veenboer C, Barker N, Klein AM, van Rheenen J, Simons BD, et al.. Intestinal crypt homeostasis results from neutral competition between symmetrically dividing Lgr5 stem cells. Cell 2010; 143:134-44; PMID:20887898; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.09.016 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barker N, Ridgway RA, van Es JH, van de Wetering M, Begthel H, van den Born M, Danenberg E, Clarke AR, Sansom OJ, Clevers H. Crypt stem cells as the cells-of-origin of intestinal cancer. Nature 2009; 457:608-11; PMID:19092804; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature07602 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bu P, Wang L, Chen KY, Srinivasan T, Murthy PK, Tung KL, Varanko AK, Chen HJ, Ai Y, King S, et al.. A miR-34a-Numb Feedforward Loop Triggered by Inflammation Regulates Asymmetric Stem Cell Division in Intestine and Colon Cancer. Cell Stem Cell 2016; 18:189-202; PMID:26849305; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2016.01.006 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hermeking H. p53 enters the microRNA world. Cancer Cell 2007; 12:414-8; PMID:17996645; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2007.10.028 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
