Spatial Distribution of the Cannabinoid Type 1 and Capsaicin Receptors May Contribute to the Complexity of Their Crosstalk
- PMID: 27653550
- PMCID: PMC5032030
- DOI: 10.1038/srep33307
Spatial Distribution of the Cannabinoid Type 1 and Capsaicin Receptors May Contribute to the Complexity of Their Crosstalk
Abstract
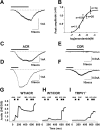
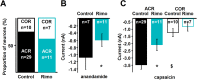
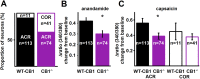
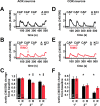
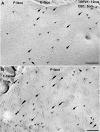
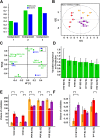
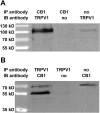
The cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) receptor and the capsaicin receptor (TRPV1) exhibit co-expression and complex, but largely unknown, functional interactions in a sub-population of primary sensory neurons (PSN). We report that PSN co-expressing CB1 receptor and TRPV1 form two distinct sub-populations based on their pharmacological properties, which could be due to the distribution pattern of the two receptors. Pharmacologically, neurons respond either only to capsaicin (COR neurons) or to both capsaicin and the endogenous TRPV1 and CB1 receptor ligand anandamide (ACR neurons). Blocking or deleting the CB1 receptor only reduces both anandamide- and capsaicin-evoked responses in ACR neurons. Deleting the CB1 receptor also reduces the proportion of ACR neurons without any effect on the overall number of capsaicin-responding cells. Regarding the distribution pattern of the two receptors, neurons express CB1 and TRPV1 receptors either isolated in low densities or in close proximity with medium/high densities. We suggest that spatial distribution of the CB1 receptor and TRPV1 contributes to the complexity of their functional interaction.
Figures

References
-
- Devane W. A. et al. Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science 258, 1946–1949 (1992). - PubMed
-
- Nagy I., Friston D., Valente J. S., Torres Perez J. V. & Andreou A. P. Pharmacology of the capsaicin receptor, transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1 ion channel. Progress in drug research. Fortschritte der Arzneimittelforschung. Progres des recherches pharmaceutiques 68, 39–76 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Mezey E. et al. Distribution of mRNA for vanilloid receptor subtype 1 (VR1), and VR1-like immunoreactivity, in the central nervous system of the rat and human. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 97, 3655–3660, 10.1073/pnas.060496197 (2000). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

