The nuclear genome of Rhazya stricta and the evolution of alkaloid diversity in a medically relevant clade of Apocynaceae
- PMID: 27653669
- PMCID: PMC5031960
- DOI: 10.1038/srep33782
The nuclear genome of Rhazya stricta and the evolution of alkaloid diversity in a medically relevant clade of Apocynaceae
Abstract
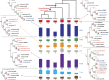
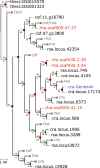
Alkaloid accumulation in plants is activated in response to stress, is limited in distribution and specific alkaloid repertoires are variable across taxa. Rauvolfioideae (Apocynaceae, Gentianales) represents a major center of structural expansion in the monoterpenoid indole alkaloids (MIAs) yielding thousands of unique molecules including highly valuable chemotherapeutics. The paucity of genome-level data for Apocynaceae precludes a deeper understanding of MIA pathway evolution hindering the elucidation of remaining pathway enzymes and the improvement of MIA availability in planta or in vitro. We sequenced the nuclear genome of Rhazya stricta (Apocynaceae, Rauvolfioideae) and present this high quality assembly in comparison with that of coffee (Rubiaceae, Coffea canephora, Gentianales) and others to investigate the evolution of genome-scale features. The annotated Rhazya genome was used to develop the community resource, RhaCyc, a metabolic pathway database. Gene family trees were constructed to identify homologs of MIA pathway genes and to examine their evolutionary history. We found that, unlike Coffea, the Rhazya lineage has experienced many structural rearrangements. Gene tree analyses suggest recent, lineage-specific expansion and diversification among homologs encoding MIA pathway genes in Gentianales and provide candidate sequences with the potential to close gaps in characterized pathways and support prospecting for new MIA production avenues.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Complete sequences of organelle genomes from the medicinal plant Rhazya stricta (Apocynaceae) and contrasting patterns of mitochondrial genome evolution across asterids.BMC Genomics. 2014 May 28;15(1):405. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-405. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24884625 Free PMC article.
-
Monoterpene indole alkaloids from Rhazya stricta.Fitoterapia. 2018 Jul;128:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2018.04.018. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Fitoterapia. 2018. PMID: 29723561
-
Gene Expression Profiling to Delineate the Anticancer Potential of a New Alkaloid Isopicrinine From Rhazya stricta.Integr Cancer Ther. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1534735420920711. doi: 10.1177/1534735420920711. Integr Cancer Ther. 2020. PMID: 32463309 Free PMC article.
-
Making iridoids/secoiridoids and monoterpenoid indole alkaloids: progress on pathway elucidation.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2014 Jun;19:35-42. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2014.03.006. Epub 2014 Apr 5. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2014. PMID: 24709280 Review.
-
Biotechnology of the medicinal plant Rhazya stricta: a little investigated member of the Apocynaceae family.Biotechnol Lett. 2017 Jun;39(6):829-840. doi: 10.1007/s10529-017-2320-7. Epub 2017 Mar 15. Biotechnol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28299544 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome size and identification of repetitive DNA sequences using low coverage sequencing in Hancornia speciosa Gomes (Apocynaceae: Gentianales).Genet Mol Biol. 2020 Nov 9;43(4):e20190175. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2019-0175. eCollection 2020. Genet Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 33170922 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Assembly and Annotation of the Medicinal Plant Calotropis gigantea, a Producer of Anticancer and Antimalarial Cardenolides.G3 (Bethesda). 2018 Feb 2;8(2):385-391. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.300331. G3 (Bethesda). 2018. PMID: 29237703 Free PMC article.
-
On the complexity of non-binary tree reconciliation with endosymbiotic gene transfer.Algorithms Mol Biol. 2023 Jul 30;18(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s13015-023-00231-5. Algorithms Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37518001 Free PMC article.
-
The Rauvolfia tetraphylla genome suggests multiple distinct biosynthetic routes for yohimbane monoterpene indole alkaloids.Commun Biol. 2023 Nov 24;6(1):1197. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05574-8. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 38001233 Free PMC article.
-
A draft genome and transcriptome of common milkweed (Asclepias syriaca) as resources for evolutionary, ecological, and molecular studies in milkweeds and Apocynaceae.PeerJ. 2019 Sep 20;7:e7649. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7649. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31579586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Luca V. D., Salim V., Atsumi S. M. & Yu F. Mining the biodiversity of plants: A revolution in the making. Science 336, 1658–1661 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Chae L., Kim T., Nilo-Poyanco R. & Rhee S. Y. Genomic signatures of specialized metabolism in plants. Science 344, 510–513 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Gilani S. A., Kikuchi A., Shinwari Z. K., Khattak Z. I. & Watanabe K. N. Phytochemical, pharmacological and ethnobotanical studies of Rhazya stricta Decne. Phytother. Res. 21, 301–307 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Smith G. N. Strictosidine: a key intermediate in the biogenesis of indole alkaloids. Chem. Commun. Lond. 912–914 (1968).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

