An Extended Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) Scheme for Rapid Direct Typing of Leptospira from Clinical Samples
- PMID: 27654037
- PMCID: PMC5031427
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004996
An Extended Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) Scheme for Rapid Direct Typing of Leptospira from Clinical Samples
Abstract
Background: Rapid typing of Leptospira is currently impaired by requiring time consuming culture of leptospires. The objective of this study was to develop an assay that provides multilocus sequence typing (MLST) data direct from patient specimens while minimising costs for subsequent sequencing.
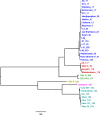
Methodology and findings: An existing PCR based MLST scheme was modified by designing nested primers including anchors for facilitated subsequent sequencing. The assay was applied to various specimen types from patients diagnosed with leptospirosis between 2014 and 2015 in the United Kingdom (UK) and the Lao Peoples Democratic Republic (Lao PDR). Of 44 clinical samples (23 serum, 6 whole blood, 3 buffy coat, 12 urine) PCR positive for pathogenic Leptospira spp. at least one allele was amplified in 22 samples (50%) and used for phylogenetic inference. Full allelic profiles were obtained from ten specimens, representing all sample types (23%). No nonspecific amplicons were observed in any of the samples. Of twelve PCR positive urine specimens three gave full allelic profiles (25%) and two a partial profile. Phylogenetic analysis allowed for species assignment. The predominant species detected was L. interrogans (10/14 and 7/8 from UK and Lao PDR, respectively). All other species were detected in samples from only one country (Lao PDR: L. borgpetersenii [1/8]; UK: L. kirschneri [1/14], L. santarosai [1/14], L. weilii [2/14]).
Conclusion: Typing information of pathogenic Leptospira spp. was obtained directly from a variety of clinical samples using a modified MLST assay. This assay negates the need for time-consuming culture of Leptospira prior to typing and will be of use both in surveillance, as single alleles enable species determination, and outbreaks for the rapid identification of clusters.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

