Placental transfusion: a review
- PMID: 27654493
- PMCID: PMC5290307
- DOI: 10.1038/jp.2016.151
Placental transfusion: a review
Abstract
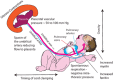
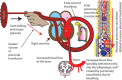
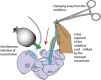
Recently there have been a number of studies and presentations on the importance of providing a placental transfusion to the newborn. Early cord clamping is an avoidable, unphysiologic intervention that prevents the natural process of placental transfusion. However, placental transfusion, although simple in concept, is affected by multiple factors, is not always straightforward to implement, and can be performed using different methods, making this basic procedure important to discuss. Here, we review three placental transfusion techniques: delayed cord clamping, intact umbilical cord milking and cut-umbilical cord milking, and the evidence in term and preterm newborns supporting this practice. We will also review several factors that influence placental transfusion, and discuss perceived risks versus benefits of this procedure. Finally, we will provide key straightforward concepts and implementation strategies to ensure that placental-to-newborn transfusion can become routine practice at any institution.
Figures


References
-
- Linderkamp O. Placental transfusion: determinants and effects. Clin Perinatol 1982; 9(3): 559–592. - PubMed
-
- Yao AC, Moinian M, Lind J. Distribution of blood between infant and placenta after birth. Lancet 1969; 2(7626): 871–873. - PubMed
-
- Brune T, Fill S, Heim G, Rabsilber A, Wohlfarth K, Garritsen HS. Quality and stability of red cells derived from gravity-separated placental blood with a hollow-fiber system. Transfusion 2007; 47(12): 2271–2275. - PubMed
-
- Aladangady N, McHugh S, Aitchison TC, Wardrop CA, Holland BM. Infants' blood volume in a controlled trial of placental transfusion at preterm delivery. Pediatrics 2006; 117(1): 93–98. - PubMed
-
- Strauss RG, Mock DM, Johnson K, Mock NI, Cress G, Knosp L et al. Circulating RBC volume, measured with biotinylated RBCs, is superior to the Hct to document the hematologic effects of delayed versus immediate umbilical cord clamping in preterm neonates. Transfusion 2003; 43(8): 1168–1172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

