A phase II randomized study of lenalidomide or lenalidomide and rituximab as maintenance therapy following standard chemotherapy for patients with high/high-intermediate risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 27654851
- PMCID: PMC5214342
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2016.255
A phase II randomized study of lenalidomide or lenalidomide and rituximab as maintenance therapy following standard chemotherapy for patients with high/high-intermediate risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
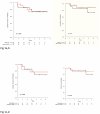
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prolonged disease-free survival in elderly relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with lenalidomide plus rituximab.Haematologica. 2016 Sep;101(9):e385-6. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2016.147256. Epub 2016 May 31. Haematologica. 2016. PMID: 27247321 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. No abstract available.
-
Lenalidomide plus R-CHOP21 in elderly patients with untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: results of the REAL07 open-label, multicentre, phase 2 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2014 Jun;15(7):730-7. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70191-3. Epub 2014 May 13. Lancet Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24831981 Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term efficacy of the combination of lenalidomide and rituximab in elderly relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients.Hematol Oncol. 2013 Dec;31(4):223-4. doi: 10.1002/hon.2049. Epub 2013 Apr 26. Hematol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23620452 Clinical Trial. No abstract available.
-
Immunomodulation therapy with lenalidomide in follicular, transformed and diffuse large B cell lymphoma: current data on safety and efficacy.J Hematol Oncol. 2013 Aug 2;6:55. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-6-55. J Hematol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23915913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two cases of permanent indwelling catheter for long-term administration of intrapleural chemotherapy.Arch Bronconeumol. 2017 Oct;53(10):590-591. doi: 10.1016/j.arbres.2017.02.009. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Arch Bronconeumol. 2017. PMID: 28359605 Review. English, Spanish. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Maintenance therapy for untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Ther Adv Hematol. 2021 May 29;12:20406207211018894. doi: 10.1177/20406207211018894. eCollection 2021. Ther Adv Hematol. 2021. PMID: 34104373 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity: immunotherapy strategies enhancing effector NK cells.Immunol Cell Biol. 2017 Apr;95(4):347-355. doi: 10.1038/icb.2017.6. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Immunol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28138156 Review.
-
[Expression of Cereblon/CRBN in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and its significance for prognosis].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Mar 14;41(3):254-256. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2020.03.013. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32311898 Free PMC article. Chinese. No abstract available.
-
Maintenance regimen of GM-CSF with rituximab and lenalidomide improves survival in high-risk B-cell lymphoma by modulating natural killer cells.Cancer Med. 2023 Jun;12(12):12975-12985. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5969. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 37081754 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular classification and therapeutics in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Feb 3;10:1124360. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1124360. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36818048 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The International Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(14):987–94. - PubMed
-
- Sehn LH, Berry B, Chhanabhai M, Fitzgerald C, Gill K, Hoskins P, et al. The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood. 2007;109(5):1857–61. - PubMed
-
- Hernandez-Ilizaliturri FJ, Reddy N, Holkova B, Ottman E, Czuczman MS. Immunomodulatory drug CC-5013 or CC-4047 and rituximab enhance antitumor activity in a severe combined immunodeficient mouse lymphoma model. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(16):5984–92. - PubMed
-
- Reddy N, Hernandez-Ilizaliturri FJ, Deeb G, Roth M, Vaughn M, Knight J, et al. Immunomodulatory drugs stimulate natural killer-cell function, alter cytokine production by dendritic cells, and inhibit angiogenesis enhancing the anti-tumour activity of rituximab in vivo. Br J Haematol. 2008;140(1):36–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources