Targeting PI3K in Cancer: Impact on Tumor Cells, Their Protective Stroma, Angiogenesis, and Immunotherapy
- PMID: 27655435
- PMCID: PMC5293166
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0716
Targeting PI3K in Cancer: Impact on Tumor Cells, Their Protective Stroma, Angiogenesis, and Immunotherapy
Abstract
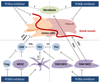
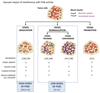
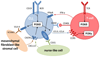
The PI3K pathway is hyperactivated in most cancers, yet the capacity of PI3K inhibitors to induce tumor cell death is limited. The efficacy of PI3K inhibition can also derive from interference with the cancer cells' ability to respond to stromal signals, as illustrated by the approved PI3Kδ inhibitor idelalisib in B-cell malignancies. Inhibition of the leukocyte-enriched PI3Kδ or PI3Kγ may unleash antitumor T-cell responses by inhibiting regulatory T cells and immune-suppressive myeloid cells. Moreover, tumor angiogenesis may be targeted by PI3K inhibitors to enhance cancer therapy. Future work should therefore also explore the effects of PI3K inhibitors on the tumor stroma, in addition to their cancer cell-intrinsic impact.
Significance: The PI3K pathway extends beyond the direct regulation of cancer cell proliferation and survival. In B-cell malignancies, targeting PI3K purges the tumor cells from their protective microenvironment. Moreover, we propose that PI3K isoform-selective inhibitors may be exploited in the context of cancer immunotherapy and by targeting angiogenesis to improve drug and immune cell delivery. Cancer Discov; 6(10); 1090-105. ©2016 AACR.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
of Potential Conflicts of Interest B.V. and K.O. are consultants for Karus Therapeutics, Oxford, UK. K.O. has received consultancy or speaker fees from Merck, GSK, Gilead and Incyte. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by M.G.
Figures

References
-
- Mayer IA, Arteaga CL. The PI3K/AKT Pathway as a Target for Cancer Treatment. Annual review of medicine. 2016;67:11–28. - PubMed
-
- Rodon J, Dienstmann R, Serra V, Tabernero J. Development of PI3K inhibitors: lessons learned from early clinical trials. Nature reviews Clinical oncology. 2013;10:143–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BBS/E/B/000C0409/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/B/000C0407/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- 095691/Z/11/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- C23338/A15965/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

