Effect of bleaching agents having a neutral pH on the surface of mineral trioxide aggregate using electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis
- PMID: 27656061
- PMCID: PMC5026102
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-0707.190004
Effect of bleaching agents having a neutral pH on the surface of mineral trioxide aggregate using electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis
Abstract
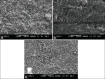
Aim: To investigate the effect of bleaching agents having a neutral pH on the surface of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) used as a coronal seal material for nonvital bleaching, beneath the bleaching agent, with the help of energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis and scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
Materials and methods: Six samples of plastic tubes filled with white MTA (Angelus white) were kept in 100% humidity for 21 days. Each sample was divided into 2 and made into 12 samples. These were then divided into three groups. Group A was exposed to Opalescence Boost 40% hydrogen peroxide (HP) (Ultradent). Group B to Opalescence 10% carbamide peroxide (Ultradent) and Group C (control group) not exposed to any bleaching agent. After recommended period of exposure to bleaching agents according to manufacturers' instructions, the samples were observed under SEM with an energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis system (JSM-6380 LA).
Results: There were no relevant changes in color and no statistically significant surface structure changes of the MTA in both the experimental groups.
Conclusion: The present findings suggest that even high concentration HP containing bleaching agents with neutral pH can be used on the surface of MTA without causing structural changes. The superior sealing ability of MTA and the high alkalinity would prevent cervical resorption postbleaching.
Keywords: Carbamide peroxide; energy-dispersive X-ray; mineral trioxide aggregate; opalescence boost; scanning electron microscopy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of intracoronal bleaching agents on the surface properties of mineral trioxide aggregate.Odontology. 2019 Oct;107(4):465-472. doi: 10.1007/s10266-019-00418-6. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Odontology. 2019. PMID: 30895486
-
Microleakage comparison of glass-ionomer and white mineral trioxide aggregate used as a coronal barrier in nonvital bleaching.Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2011 Nov 1;16(7):e1017-21. doi: 10.4317/medoral.17306. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2011. PMID: 21743399
-
Tooth discoloration after the use of new pozzolan cement (Endocem) and mineral trioxide aggregate and the effects of internal bleaching.J Endod. 2013 Dec;39(12):1598-602. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2013.08.035. Epub 2013 Oct 6. J Endod. 2013. PMID: 24238455
-
Effect of three bleaching agents on the surface properties of three different esthetic restorative materials.J Prosthet Dent. 2003 May;89(5):466-73. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3913(03)00105-7. J Prosthet Dent. 2003. PMID: 12806324
-
Scanning Electron Microscopy and Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Microanalysis of Set CEM Cement after Application of Different Bleaching Agents.Iran Endod J. 2017 Spring;12(2):191-195. doi: 10.22037/iej.2017.37. Iran Endod J. 2017. PMID: 28512484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lado EA, Stanley HR, Weisman MI. Cervical resorption in bleached teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1983;55:78–80. - PubMed
-
- Montgomery S, Texas A. External cervical resorption after bleaching a pulpless tooth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1984;57:203–6. - PubMed
-
- Brito-Junior M, Faria-e-Silva AL, Fonseca B, Camilo CC. Sealing ability of MTA used as cervical barrier in intracoronal bleaching. Acta Odontol Latinoam. 2009;22:118–22. - PubMed
-
- Vosoughhosseini S, Lotfi M, Shahmoradi K, Saghiri MA, Zand V, Mehdipour M, et al. Microleakage comparison of glass-ionomer and white mineral trioxide aggregate used as a coronal barrier in nonvital bleaching. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2011;16:e1017–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous