Influence of Child Factors on Health-Care Professionals' Recognition of Common Childhood Mental-Health Problems
- PMID: 27656089
- PMCID: PMC5016556
- DOI: 10.1007/s10826-016-0475-9
Influence of Child Factors on Health-Care Professionals' Recognition of Common Childhood Mental-Health Problems
Abstract
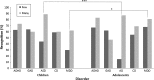
Early recognition of childhood mental-health problems can help minimise long-term negative outcomes. Recognition of mental-health problems, needed for referral and diagnostic evaluation, is largely dependent on health-care professionals' (HCPs) judgement of symptoms presented by the child. This study aimed to establish whether HCPs recognition of mental-health problems varies as a function of three child-related factors (type of problem, number of symptoms, and demographic characteristics). In an online survey, HCPs (n = 431) evaluated a series of vignettes describing children with symptoms of mental-health problems. Vignettes varied by problem type (Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), Generalised Anxiety Disorder (GAD), Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), Conduct Disorder (CD) and Major Depressive Disorder), number of symptoms presented (few and many), and child demographic characteristics (ethnicity, gender, age and socio-economic status (SES)). Results show that recognition of mental-health problems varies by problem type, with ADHD best recognised and GAD worst. Furthermore, recognition varies by the number of symptoms presented. Unexpectedly, a child's gender, ethnicity and family SES did not influence likelihood of problem recognition. These results are the first to reveal differences in HCPs' recognition of various common childhood mental-health problems. HCPs in practice should be advised about poor recognition of GAD, and superior recognition of ADHD, if recognition of all childhood mental-health problems is to be equal.
Keywords: Children; Demographic characteristics; Health-care professionals; Mental-health problems; Recognition; Symptoms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- American Psychological Association (APA) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4, text revision. Washington, DC: Author; 2000.
-
- American Psychological Association (APA) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5. Arlington, VA: Author; 2013.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
