Molecular Biology and Infection of Hepatitis E Virus
- PMID: 27656178
- PMCID: PMC5013053
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01419
Molecular Biology and Infection of Hepatitis E Virus
Abstract
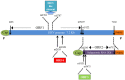
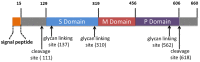
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) is a viral pathogen transmitted primarily via fecal-oral route. In humans, HEV mainly causes acute hepatitis and is responsible for large outbreaks of hepatitis across the world. The case fatality rate of HEV-induced hepatitis ranges from 0.5 to 3% in young adults and up to 30% in infected pregnant women. HEV strains infecting humans are classified into four genotypes. HEV strains from genotypes 3 and 4 are zoonotic, whereas those from genotypes 1 and 2 have no known animal reservoirs. Recently, notable progress has been accomplished for better understanding of HEV biology and infection, such as chronic HEV infection, in vitro cell culture system, quasi-enveloped HEV virions, functions of the HEV proteins, mechanism of HEV antagonizing host innate immunity, HEV pathogenesis and vaccine development. However, further investigation on the cross-species HEV infection, host tropism, vaccine efficacy, and HEV-specific antiviral strategy is still needed. This review mainly focuses on molecular biology and infection of HEV and offers perspective new insight of this enigmatic virus.
Keywords: HEV; HEV biology; HEV infection; HEV vaccine; hepatitis E virus; viral proteins of HEV.
Figures
References
-
- Abes S., Moulton H. M., Clair P., Prevot P., Youngblood D. S., Wu R. P., et al. (2006). Vectorization of morpholino oligomers by the (R-Ahx-R)4 peptide allows efficient splicing correction in the absence of endosomolytic agents. J. Control. Release 116 304–313. 10.1016/j.jconrel.2006.09.011 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

