Novel BRCA2-Interacting Protein, LIMD1, Is Essential for the Centrosome Localization of BRCA2 in Esophageal Cancer Cell
- PMID: 27656835
- PMCID: PMC7838625
- DOI: 10.3727/096504016X14652175055765
Novel BRCA2-Interacting Protein, LIMD1, Is Essential for the Centrosome Localization of BRCA2 in Esophageal Cancer Cell
Abstract
Mutation of breast cancer 2, early onset (BRCA2) has been identified as a vital risk factor for esophageal cancer (EC). To date, several proteins have been reported as BRCA2-interacting proteins and are associated with multiple biological processes. This study's aim was to identify a novel interactive protein of BRCA2 and to explore its functional roles in EC. A yeast two-hybrid screening was performed to identify a novel BRCA2-interacting protein. Glutathione-S-transferase (GST) pull-down analysis was performed to find out how the binding domain of BRCA2 interacts with LIM domains containing 1 (LIMD1). The interaction between LIMD1 and BRCA2 at the endogenous level was confirmed by using coimmunoprecipitation and immunobloting. Furthermore, two different sequences of short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) against LIMD1 were transfected into the human EC cell line ECA109. Afterward, the effects of LIMD1 suppression on the centrosome localization of BRCA2 and cell division were analyzed using an immunofluorescence microscope. Results showed that LIMD1 was a novel BRCA2-interacting protein, and LIMD1 interacted with the conserved region of BRCA2 (amino acids 2,750-3,094) in vitro. Importantly, after interfering with the protein expression of LIMD1 in ECA109 cells, the centrosome localization of BRCA2 was significantly abolished and abnormal cell division was significantly increased. These results suggested that LIMD1 is a novel BRCA2-interacting protein and is involved in the centrosome localization of BRCA2 and suppression of LIMD1, causing abnormal cell division in EC cells.
Figures

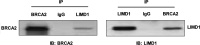
Similar articles
-
WTIP interacts with BRCA2 and is essential for BRCA2 centrosome localization in cervical cancer cell.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2016 Nov;294(6):1311-1316. doi: 10.1007/s00404-016-4176-9. Epub 2016 Aug 18. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2016. PMID: 27535760
-
LIMD1 antagonizes E2F1 activity and cell cycle progression by enhancing Rb function in cancer cells.Cell Biol Int. 2014 Jul;38(7):809-17. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10266. Epub 2014 Feb 27. Cell Biol Int. 2014. PMID: 24523249
-
BRCA2 mediates centrosome cohesion via an interaction with cytoplasmic dynein.Cell Cycle. 2016 Aug 17;15(16):2145-2156. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1195531. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 27433848 Free PMC article.
-
[Recent advances in PLK1 and breast cancer].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Jun;40(6):427-9. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21914359 Review. Chinese. No abstract available.
-
A comprehensive analysis of BRCA2 gene: focus on mechanistic aspects of its functions, spectrum of deleterious mutations, and therapeutic strategies targeting BRCA2-deficient tumors.Med Oncol. 2018 Jan 31;35(3):18. doi: 10.1007/s12032-018-1085-8. Med Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29387975 Review.
Cited by
-
LIMD1 is a survival prognostic marker of gastric cancer and hinders tumor progression by suppressing activation of YAP1.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Oct 9;10:4349-4361. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S174856. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 30349368 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of LIMD1 promotes proliferation and reverses cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.Oncol Lett. 2019 Mar;17(3):2993-3000. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.9921. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 30854077 Free PMC article.
-
Differential transmission of the molecular signature of RBSP3, LIMD1 and CDC25A in basal/ parabasal versus spinous of normal epithelium during head and neck tumorigenesis: A mechanistic study.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 19;13(4):e0195937. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195937. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29672635 Free PMC article.
-
A HIF-LIMD1 negative feedback mechanism mitigates the pro-tumorigenic effects of hypoxia.EMBO Mol Med. 2018 Aug;10(8):e8304. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201708304. EMBO Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29930174 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
