Protein Kinases and Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 27657053
- PMCID: PMC5037850
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17091585
Protein Kinases and Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
Currently, the lack of new drug candidates for the treatment of major neurological disorders such as Parkinson's disease has intensified the search for drugs that can be repurposed or repositioned for such treatment. Typically, the search focuses on drugs that have been approved and are used clinically for other indications. Kinase inhibitors represent a family of popular molecules for the treatment and prevention of various cancers, and have emerged as strong candidates for such repurposing because numerous serine/threonine and tyrosine kinases have been implicated in the pathobiology of Parkinson's disease. This review focuses on various kinase-dependent pathways associated with the expression of Parkinson's disease pathology, and evaluates how inhibitors of these pathways might play a major role as effective therapeutic molecules.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; dopamine; kinase inhibitors; serine/threonine kinase; tyrosine kinase.
Conflict of interest statement
The findings and conclusions found herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the views of the FDA. The mention of the trade names or commercial products does not constitute endorsement.
Figures
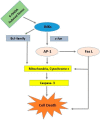
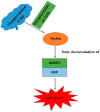
References
-
- Imam S.Z., Zhou Q., Yamamoto A., Valente A.J., Ali S.F., Bains M., Roberts J.L., Kahle P.J., Clark R.A., Li S.L. Novel regulation of parkin function through c-Abl-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation: Implications for Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2011;31:157–163. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1833-10.2011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

