Fabrication of Micro-Needle Electrodes for Bio-Signal Recording by a Magnetization-Induced Self-Assembly Method
- PMID: 27657072
- PMCID: PMC5038806
- DOI: 10.3390/s16091533
Fabrication of Micro-Needle Electrodes for Bio-Signal Recording by a Magnetization-Induced Self-Assembly Method
Abstract
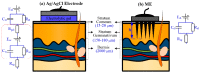
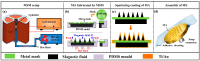
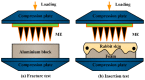
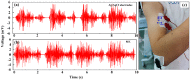
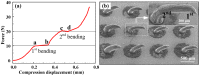
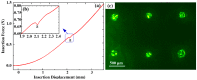
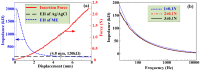
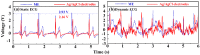
Micro-needle electrodes (MEs) have attracted more and more attention for monitoring physiological electrical signals, including electrode-skin interface impedance (EII), electromyography (EMG) and electrocardiography (ECG) recording. A magnetization-induced self-assembling method (MSM) was developed to fabricate a microneedle array (MA). A MA coated with Ti/Au film was assembled as a ME. The fracture and insertion properties of ME were tested by experiments. The bio-signal recording performance of the ME was measured and compared with a typical commercial wet electrode (Ag/AgCl electrode). The results show that the MA self-assembled from the magnetic droplet array under the sum of gravitational surface tension and magnetic potential energies. The ME had good toughness and could easily pierce rabbit skin without being broken or buckling. When the compression force applied on the ME was larger than 2 N, ME could stably record EII, which was a lower value than that measured by Ag/AgCl electrodes. EMG signals collected by ME varied along with the contraction of biceps brachii muscle. ME could record static ECG signals with a larger amplitude and dynamic ECG signals with more distinguishable features in comparison with a Ag/AgCl electrode, therefore, ME is an alternative electrode for bio-signal monitoring in some specific situations.
Keywords: ECG; EMG; electrode; impedance; insertion; magnetization-induced self-assembling; micro-needle array.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Zhou W., Cheng D.C., Song R., Zhang C.J., Xu W.P., Pan X.L. Characterization of alternating current impedance properties of biomedical electrodes. J. Cent. South Univ. 2013;20:1254–1258. doi: 10.1007/s11771-013-1609-5. - DOI
-
- Hoffmann K.P., Ruff R. Flexible dry surface-electrodes for ECG long-term monitoring; Proceedings of the 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society; Lyon, France. 22–26 August 2007; pp. 5740–5743. - PubMed
-
- Forvi E., Bedoni M., Carabalona R., Soncini M., Mazzoleni P., Rizzo F., O’Mahony C., Morasso C., Cassarà D.G., Gramatica F. Preliminary technological assessment of microneedles-based dry electrodes for biopotential monitoring in clinical examinations. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012;180:177–186. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2012.04.019. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

