DNA Polymerase θ: A Unique Multifunctional End-Joining Machine
- PMID: 27657134
- PMCID: PMC5042397
- DOI: 10.3390/genes7090067
DNA Polymerase θ: A Unique Multifunctional End-Joining Machine
Abstract
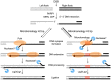
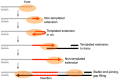
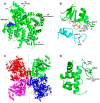
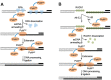
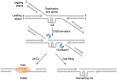
The gene encoding DNA polymerase θ (Polθ) was discovered over ten years ago as having a role in suppressing genome instability in mammalian cells. Studies have now clearly documented an essential function for this unique A-family polymerase in the double-strand break (DSB) repair pathway alternative end-joining (alt-EJ), also known as microhomology-mediated end-joining (MMEJ), in metazoans. Biochemical and cellular studies show that Polθ exhibits a unique ability to perform alt-EJ and during this process the polymerase generates insertion mutations due to its robust terminal transferase activity which involves template-dependent and independent modes of DNA synthesis. Intriguingly, the POLQ gene also encodes for a conserved superfamily 2 Hel308-type ATP-dependent helicase domain which likely assists in alt-EJ and was reported to suppress homologous recombination (HR) via its anti-recombinase activity. Here, we review our current knowledge of Polθ-mediated end-joining, the specific activities of the polymerase and helicase domains, and put into perspective how this multifunctional enzyme promotes alt-EJ repair of DSBs formed during S and G2 cell cycle phases.
Keywords: DNA polymerase; DNA repair; alternative end-joining; cancer; genome instability; microhomology-mediated end-joining; replication repair.
Conflict of interest statement
R.T.P. has filed provisional patents on the use of Polθ for modifying the 3’ ends of nucleic acids and expanded-size nucleotide analogs as Polθ inhibitors and cancer therapeutics.
Figures


References
-
- Goff J.P., Shields D.S., Seki M., Choi S., Epperly M.W., Dixon T., Wang H., Bakkenist C.J., Dertinger S.D., Torous D.K., et al. Lack of DNA polymerase theta (POLQ) radiosensitizes bone marrow stromal cells in vitro and increases reticulocyte micronuclei after total-body irradiation. Radiat. Res. 2009;172:165–174. doi: 10.1667/RR1598.1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Higgins G.S., Prevo R., Lee Y.F., Helleday T., Muschel R.J., Taylor S., Yoshimura M., Hickson I.D., Bernhard E.J., McKenna W.G. A small interfering RNA screen of genes involved in DNA repair identifies tumor-specific radiosensitization by POLQ knockdown. Cancer Res. 2010;70:2984–2993. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4040. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

