Hepatitis C Treatment and Barriers to Eradication
- PMID: 27657495
- PMCID: PMC5288596
- DOI: 10.1038/ctg.2016.50
Hepatitis C Treatment and Barriers to Eradication
Abstract
Current treatment for chronic hepatitis C (CHC) is highly efficacious, well-tolerated, and of short duration for the majority of patients. Despite the dramatic advances in therapy, there remain several barriers to disease eradication. These include deficiencies in screening, diagnosis, and access to care, and high cost of the direct-acting antiviral medications. In addition, incident cases and reinfection associated with injection drug use contribute to the persistent worldwide disease burden. This article will review the current CHC treatments, and outline the remaining gaps in therapy and barriers to disease eradication.
Figures
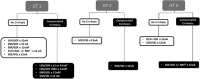

References
-
- AASLD-IDSA. Recommendations for Testing, Managing, and Treating Hepatitis C; http://www.hcvguidelines.org.
-
- Afdhal N, Zeuzem S, Kwo P et al. Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir for untreated HCV genotype 1 infection. N Engl J Med 2014; 370: 1889–1898. - PubMed
-
- Zeuzem S, Ghalib R, Reddy KR et al. Grazoprevir-elbasvir combination therapy for treatment-naive cirrhotic and noncirrhotic patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1, 4, or 6 infection: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2015; 163: 1–13. - PubMed
-
- Zeuzem S, Dusheiko GM, Salupere R et al. Sofosbuvir and ribavirin in HCV genotypes 2 and 3. N Engl J Med 2014; 370: 1993–2001. - PubMed
-
- Sulkowski MS, Gardiner DF, Rodriguez-Torres M et al. Daclatasvir plus sofosbuvir for previously treated or untreated chronic HCV infection. N Engl J Med 2014; 370: 211–221. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

