A Rationally Designed TNF-α Epitope-Scaffold Immunogen Induces Sustained Antibody Response and Alleviates Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice
- PMID: 27658047
- PMCID: PMC5033357
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163080
A Rationally Designed TNF-α Epitope-Scaffold Immunogen Induces Sustained Antibody Response and Alleviates Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice
Abstract
The TNF-α biological inhibitors have significantly improved the clinical outcomes of many autoimmune diseases, in particular rheumatoid arthritis. However, the practical uses are limited due to high costs and the risk of anti-drug antibody responses. Attempts to develop anti-TNF-α vaccines have generated encouraging data in animal models, however, data from clinical trials have not met expectations. In present study, we designed a TNF-α epitope-scaffold immunogen DTNF7 using the transmembrane domain of diphtheria toxin, named DTT as a scaffold. Molecular dynamics simulation shows that the grafted TNF-α epitope is entirely surface-exposed and presented in a native-like conformation while the rigid helical structure of DTT is minimally perturbed, thereby rendering the immunogen highly stable. Immunization of mice with alum formulated DTNF7 induced humoral responses against native TNF-α, and the antibody titer was sustained for more than 6 months, which supports a role of the universal CD4 T cell epitopes of DTT in breaking self-immune tolerance. In a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis, DTNF7-alum vaccination markedly delayed the onset of collagen-induced arthritis, and reduced incidence as well as clinical score. DTT is presumed safe as an epitope carrier because a catalytic inactive mutant of diphtheria toxin, CRM197 has good clinical safety records as an active vaccine component. Taken all together, we show that DTT-based epitope vaccine is a promising strategy for prevention and treatment of autoimmune diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the author of this manuscript has the following competing interests: Li Deng is an employee of Shanghai HyCharm Inc. Shanghai HyCharm Inc has patented the methods of immunogen design (number WO2014/183649A1), and planned to develop an optimized version of TNF-α therapeutic vaccine. This does not alter the author’s adherence to all the PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
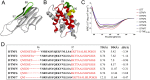
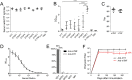
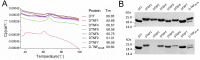
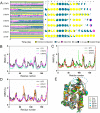


Comment in
-
Rheumatoid arthritis: Paving the way for TNF vaccines.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016 Dec;12(12):692. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.171. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 27733760 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The Immunogenicity and Anti-Tumor Efficacy of a Rationally Designed EGFR Vaccine.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(1):46-56. doi: 10.1159/000488408. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29566364
-
Aldehyde modification and alum coadjuvancy enhance anti-TNF-α autovaccination and mitigate arthritis in rat.J Pept Sci. 2015 May;21(5):400-7. doi: 10.1002/psc.2718. Epub 2014 Nov 26. J Pept Sci. 2015. PMID: 25424319
-
Active immunisation targeting soluble murine tumour necrosis factor alpha is safe and effective in collagen-induced arthritis model treatment.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016 Mar-Apr;34(2):242-6. Epub 2016 Jan 20. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26811933
-
Rheumatoid arthritis vaccine therapies: perspectives and lessons from therapeutic ligand epitope antigen presentation system vaccines for models of rheumatoid arthritis.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2015 Jun;14(6):891-908. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2015.1026330. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2015. PMID: 25787143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies for active TNF-α vaccination in rheumatoid arthritis treatment.Vaccine. 2013 Aug 28;31(38):4063-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.06.101. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23845805 Review.
Cited by
-
Self-assembling peptides as immunomodulatory biomaterials.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Mar 1;11:1139782. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1139782. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36937769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of built-in adjuvants for epitope-based vaccines.PeerJ. 2019 Jan 14;6:e6185. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6185. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 30656066 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant Costimulatory Fusion Proteins as Functional Immunomodulators Enhance Antitumor Activity in Murine B16F10 Melanoma.Vaccines (Basel). 2020 May 14;8(2):223. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8020223. Vaccines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32423130 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Targeting Can Protect against Arthritis with Low Sensitization to Infection.Front Immunol. 2017 Nov 14;8:1533. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01533. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29184553 Free PMC article.
-
The Immunogenicity and Anti-tumor Efficacy of a Rationally Designed Neoantigen Vaccine for B16F10 Mouse Melanoma.Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 5;10:2472. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02472. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31749795 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feldmann M, Maini RN. TNF defined as a therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases Nature medicine. 2003;9(11):1433-. . - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

