Sumoylation of IkB attenuates NF-kB-induced nitrosative stress at rostral ventrolateral medulla and cardiovascular depression in experimental brain death
- PMID: 27658615
- PMCID: PMC5034413
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-016-0283-y
Sumoylation of IkB attenuates NF-kB-induced nitrosative stress at rostral ventrolateral medulla and cardiovascular depression in experimental brain death
Abstract
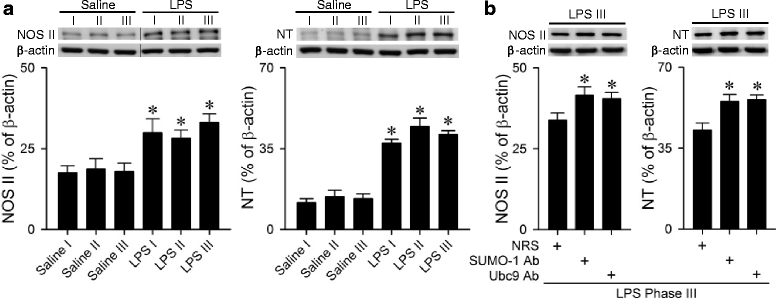
Background: Small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) is a group of proteins that participates in post-translational modifications. One known SUMO target is the transcription factor nuclear factor-kB (NF-kB) that plays a pivotal role in many disease processes; sumoylation inactivates NF-kB by conjugation with inhibitors of NF-kB (IkB). Our laboratory demonstrated previously that transcriptional upregulation of nitric oxide synthase II (NOS II) by NF-kB, leading to nitrosative stress by the formation of peroxynitrite in the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM), underpins the defunct brain stem cardiovascular regulation that precedes brain death. Based on an experimental endotoxemia model, this study evaluated the hypothesis that sumoylation plays a pro-life role in brain death by interacting with the NF-kB/NOS II/peroxynitrite signaling pathway in the RVLM.
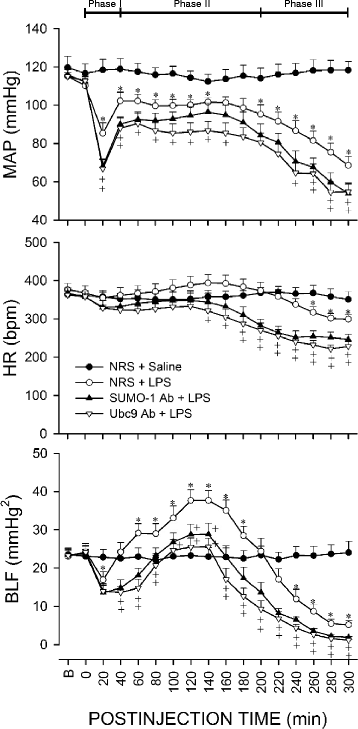
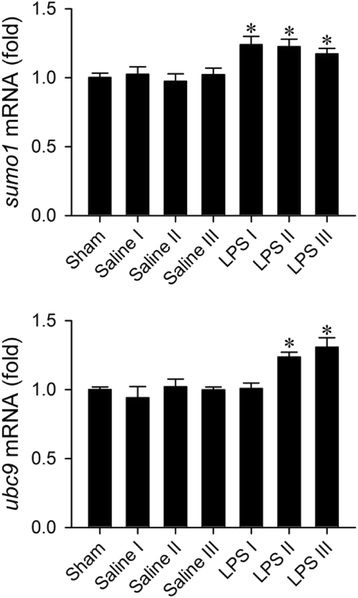
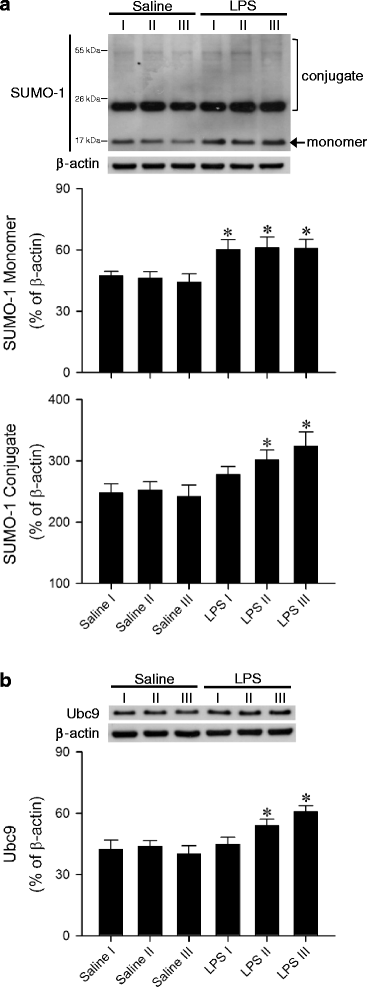
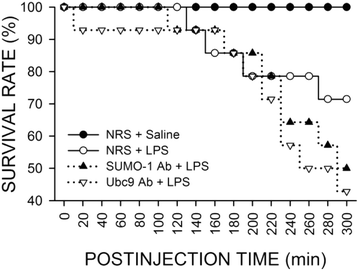
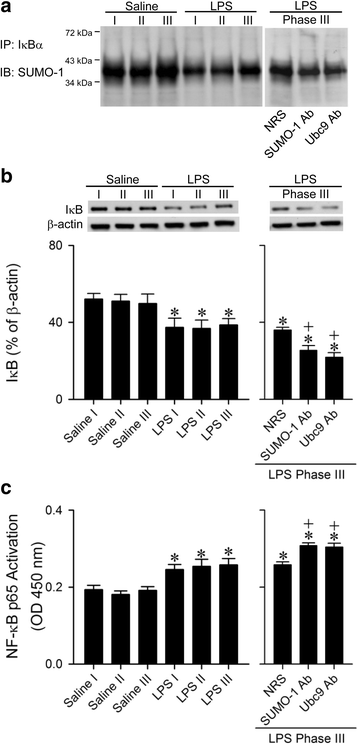
Results: In Sprague-Dawley rats, intravenous administration of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 10 mg kg-1) elicited an augmentation of SUMO-1 and ubiquitin-conjugase 9 (Ubc9) mRNA or protein levels, alongside SUMO-1-conjugated proteins in the RVLM. Immunoneutralization of SUMO-1 or Ubc9 in the RVLM significantly potentiated the already diminished sumoylation of IkBα and intensified NF-kB activation and NOS II/peroxynitrite expression in this brain stem substrate, together with exacerbated fatality, cardiovascular depression and reduction of an experimental index of a life-and-death signal detected from arterial pressure that disappears in comatose patients signifying failure of brain stem cardiovascular regulation before brain death.
Conclusion: We conclude that sumoylation of IkB in the RVLM ameliorates the defunct brain stem cardiovascular regulation that underpins brain death in our experimental endotoxemia modal by reducing nitrosative stress via inhibition of IkB degradation that diminishes the induction of the NF-kB/NOS II/peroxynitrite signaling cascade.
Keywords: Defunct brain stem cardiovascular regulation; Nitrosative stress; Rostral ventrolateral medulla; Small ubiquitin-related modifier; Ubiquitin-conjugase 9.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sumoylation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α ameliorates failure of brain stem cardiovascular regulation in experimental brain death.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 3;6(3):e17375. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017375. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21390240 Free PMC article.
-
A double-edged sword role for ubiquitin-proteasome system in brain stem cardiovascular regulation during experimental brain death.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27404. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027404. Epub 2011 Nov 14. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22110641 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional up-regulation of nitric oxide synthase II by nuclear factor-kappaB at rostral ventrolateral medulla in a rat mevinphos intoxication model of brain stem death.J Physiol. 2007 Jun 15;581(Pt 3):1293-307. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.130872. Epub 2007 Mar 29. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17395621 Free PMC article.
-
PTEN/FLJ10540/PI3K/Akt cascade in experimental brain stem death: A newfound role for a classical tumorigenic signaling pathway.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Sep;155:207-212. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.07.002. Epub 2018 Jul 3. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30008438 Review.
-
Differential impacts of brain stem oxidative stress and nitrosative stress on sympathetic vasomotor tone.Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Sep;201:120-136. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.05.015. Epub 2019 May 31. Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31153955 Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel De Novo NFKBIA Missense Mutation Associated to Ectodermal Dysplasia with Dysgammaglobulinemia.Genes (Basel). 2022 Oct 19;13(10):1900. doi: 10.3390/genes13101900. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292785 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Functional Connectivity Between Medulla and Inferior Parietal Cortex in Medication-Free Major Depressive Disorder.Front Neurosci. 2018 Dec 10;12:926. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00926. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30618555 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of microRNA-301b accelerates hippocampal microglia activation and cognitive impairment in mice with depressive-like behavior through the NF-κB signaling pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Apr 8;10(4):316. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1522-4. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 30962417 Free PMC article.
-
HOPS/Tmub1 involvement in the NF-kB-mediated inflammatory response through the modulation of TRAF6.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Oct 15;11(10):865. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03086-5. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 33060567 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-Dependent Acute Circulatory Fates Elicited by Cadmium Are Mediated by Differential Engagements of Cardiovascular Regulatory Mechanisms in Brain.Front Physiol. 2019 Jun 18;10:772. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00772. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31275174 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

