Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Load Response to 2 Antiviral Regimens, Tenofovir/Lamivudine and Lamivudine, in HIV/ HBV-Coinfected Pregnant Women in Guangxi, China: The Tenofovir in Pregnancy (TiP) Study
- PMID: 27658693
- PMCID: PMC11264234
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiw439
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Load Response to 2 Antiviral Regimens, Tenofovir/Lamivudine and Lamivudine, in HIV/ HBV-Coinfected Pregnant Women in Guangxi, China: The Tenofovir in Pregnancy (TiP) Study
Abstract
Background: There is limited information on antiviral therapy for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection among pregnant women coinfected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and HBV.
Methods: A phase 2 randomized, controlled trial of a regimen containing tenofovir (TDF)/lamivudine (3TC) and a regimen containing 3TC in HIV/HBV-coinfected pregnant women in China. The HBV virological response was compared in study arms.
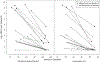
Results: The median decline in the HBV DNA level was 2.60 log10 copies/mL in the TDF/3TC arm and 2.24 log10 copies/mL in the 3TC arm (P = .41). All women achieved HBV DNA levels of <6 log10 copies/mL at delivery.
Conclusions: Initiation of either regimen led to achievement of HBV DNA levels below the threshold associated with perinatal HBV transmission.
Clinical trials registration: NCT01125696.
Keywords: HBV DNV viral load; HBV suppression; HIV/HBV coinfection; lamivudine; pregnancy; tenofovir.
Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America 2016. This work is written by (a) US Government employee(s) and is in the public domain in the US.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Hoffmann CJ, Thio CL. Clinical implications of HIV and hepatitis B co-infection in Asia and Africa. Lancet Infect Dis 2007; 7:402–9. - PubMed
-
- Thio CL, Locarnini S. Treatment of HIV/HBV coinfection: clinical and virologic issues. AIDS Rev 2007; 9:40–53. - PubMed
-
- Liang X, Bi S, Yang W, et al. Epidemiological serosurvey of hepatitis B in China–declining HBV prevalence due to hepatitis B vaccination. Vaccine 2009; 27:6550–7. - PubMed
-
- Xu H, Zeng T, Liu JY, et al. Measures to reduce mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B virus in China: a meta-analysis. Dig Dis Sci 2014; 59:242–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical