Bacterial Abscess Formation Is Controlled by the Stringent Stress Response and Can Be Targeted Therapeutically
- PMID: 27658736
- PMCID: PMC5078632
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.09.015
Bacterial Abscess Formation Is Controlled by the Stringent Stress Response and Can Be Targeted Therapeutically
Abstract
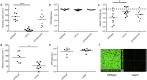
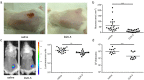
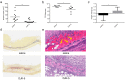
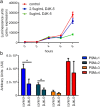
Cutaneous abscess infections are difficult to treat with current therapies and alternatives to conventional antibiotics are needed. Understanding the regulatory mechanisms that govern abscess pathology should reveal therapeutic interventions for these recalcitrant infections. Here we demonstrated that the stringent stress response employed by bacteria to cope and adapt to environmental stressors was essential for the formation of lesions, but not bacterial growth, in a methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) cutaneous abscess mouse model. To pharmacologically confirm the role of the stringent response in abscess formation, a cationic peptide that causes rapid degradation of the stringent response mediator, guanosine tetraphosphate (ppGpp), was employed. The therapeutic application of this peptide strongly inhibited lesion formation in mice infected with Gram-positive MRSA and Gram-negative Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Overall, we provide insights into the mechanisms governing abscess formation and a paradigm for treating multidrug resistant cutaneous abscesses.
Keywords: Cationic peptide; DJK-5; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Staphylococcus aureus; ppGpp.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Aberg A., Shingler V., Balsalobre C. (p)ppGpp regulates type 1 fimbriation of Escherichia coli by modulating the expression of the site-specific recombinase FimB. Mol. Microbiol. 2006;60:1520–1533. - PubMed
-
- Bolouri H., Savman K., Wang W., Thomas A., Maurer N., Dullaghan E., Fjell C.D., Ek C.J., Hagberg H., Hancock R.E.W. Innate defense regulator peptide 1018 protects against perinatal brain injury. Ann. Neurol. 2014;75:395–410. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter J.L. Klebsiella pulmonary infections: occurrence at one medical center and review. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1990;12:672–682. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

