TYROBP genetic variants in early-onset Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 27658901
- PMCID: PMC5159294
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2016.07.028
TYROBP genetic variants in early-onset Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
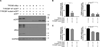
We aimed to identify new candidate genes potentially involved in early-onset Alzheimer's disease (EOAD). Exome sequencing was conducted on 45 EOAD patients with either a family history of Alzheimer's disease (AD, <65 years) or an extremely early age at the onset (≤55 years) followed by multiple variant filtering according to different modes of inheritance. We identified 29 candidate genes potentially involved in EOAD, of which the gene TYROBP, previously implicated in AD, was selected for genetic and functional follow-up. Using 3 patient cohorts, we observed rare coding TYROBP variants in 9 out of 1110 EOAD patients, whereas no such variants were detected in 1826 controls (p = 0.0001), suggesting that at least some rare TYROBP variants might contribute to EOAD risk. Overexpression of the p.D50_L51ins14 TYROBP mutant led to a profound reduction of TREM2 expression, a well-established risk factor for AD. This is the first study supporting a role for genetic variation in TYROBP in EOAD, with in vitro support for a functional effect of the p.D50_L51ins14 TYROBP mutation on TREM2 expression.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Burden test; Exome sequencing; TREM2; TYROBP.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
statement The authors declare have no conflicts of interest to disclose. The ethics committees of all participating institutions have approved this study.
Figures

References
-
- Brckalo T, Calzetti F, Perez-Cabezas B, Borras FE, Cassatella MA, Lopez-Botet M. Functional analysis of the CD300e receptor in human monocytes and myeloid dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol. 2010;40:722–732. - PubMed
-
- Cruchaga C, Karch CM, Jin SC, Benitez BA, Cai Y, Guerreiro R, Harari O, Norton J, Budde J, Bertelsen S, Jeng AT, Cooper B, Skorupa T, Carrell D, Levitch D, Hsu S, Choi J, Ryten M, Hardy J, Trabzuni D, Weale ME, Ramasamy A, Smith C, Sassi C, Bras J, Gibbs JR, Hernandez DG, Lupton MK, Powell J, Forabosco P, Ridge PG, Corcoran CD, Tschanz JT, Norton MC, Munger RG, Schmutz C, Leary M, Demirci FY, Bamne MN, Wang X, Lopez OL, Ganguli M, Medway C, Turton J, Lord J, Braae A, Barber I, Brown K, Passmore P, Craig D, Johnston J, McGuinness B, Todd S, Heun R, Kolsch H, Kehoe PG, Hooper NM, Vardy ER, Mann DM, Pickering-Brown S, Kalsheker N, Lowe J, Morgan K, David Smith A, Wilcock G, Warden D, Holmes C, Pastor P, Lorenzo-Betancor O, Brkanac Z, Scott E, Topol E, Rogaeva E, Singleton AB, Kamboh MI, St George-Hyslop P, Cairns N, Morris JC, Kauwe JS, Goate AM. Rare coding variants in the phospholipase D3 gene confer risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Nature. 2014;505:550–554. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

