Chemical Modification of Ginsenoside on Cell Viability and Cytokine Secretion
- PMID: 27659265
- PMCID: PMC5425158
- DOI: 10.2174/1874609809666160920125803
Chemical Modification of Ginsenoside on Cell Viability and Cytokine Secretion
Abstract
Background: Rb1 is a ginsenoside steroid glycoside found exclusively in the plant Panax ginseng. In an earlier report, we showed that Rb1 increased cell proliferation and reduced VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) secretion by human retinal pigment epithelial (ARPE19) cells.
Objective: In the present study, we hypothesized that chemical modification of Rb1 changes the level of VEGF secretion by ARPE19 cells.
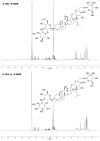
Method: Three derivatives of Rb1 were chemically synthesized by hydrogenation (Rb1-H2), acetylation (Rb1-Acyl), and epoxidation (Rb1-Epoxy). Structural modifications were confirmed by 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectra and Mass Spectrometry (MS). To test the biological activity, chemically modified compounds were added to cell culture media and incubated for 72 hours at a concentration of 250 nM at 37°C. Conditioned media were collected and cells were harvested/ counted after treatment. Viable cell numbers were determined by the trypan blue dye exclusion method and VEGF levels by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays (ELISA).
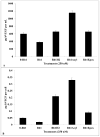
Results: Consistent with the prior report, results of the present study show Rb1 increased cell proliferation and decreased VEGF secretion. Similar to Rb1's effect on cell proliferation, treatment with Rb1-H2, Rb1-Acyl and Rb1-Epoxy resulted in an increase in cell numbers. In contrast to Rb1- induced decrease in VEGF secretion, treatment with Rb1-H2, Rb-Acyl and Rb1-Epoxy resulted in increased VEGF levels.
Conclusion: Chemical modifications of the ginsenoside Rb1 significantly affect the biological activity of VEGF secretion by ARPE19 cells. Additional SAR (Structure Activity Relationship) experiments will be conducted to study the detailed mechanisms by which how specific modifications of Rb1 functional groups alter biological activities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that this article content has no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Fulder S. The Book of Ginseng and other Chinese Herbs for Vitality. Rochester: Healing Arts Press; 1993.
-
- Nocerino E, Amato M, Izzo AA. The aphrodisiac and adaptogenic properties of ginseng. Fitoterapia. 2000;71(Suppl 1):S1–5. - PubMed
-
- Pardianto G. Understanding diabetic retinopathy. Mimbar Ilmiah Oftalmologi Indonesia. 2005;2:65–6.
-
- Einwallner E, Ahlers C, Golbaz I, et al. Neovascular age related macular degeneration under anti-angiogenic therapy: Subretinal fluid is a relevant prognostic parameter. Ophthalmologie. 2010;107(2):158–64. - PubMed
-
- Evans JR. Risk Factors for age-related macular degeneration. Prog Retinal Eye Res. 2001;20(2):227–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

