Anti-ageing active ingredients from herbs and nutraceuticals used in traditional Chinese medicine: pharmacological mechanisms and implications for drug discovery
- PMID: 27659301
- PMCID: PMC5429334
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13631
Anti-ageing active ingredients from herbs and nutraceuticals used in traditional Chinese medicine: pharmacological mechanisms and implications for drug discovery
Abstract
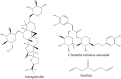
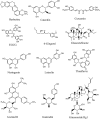
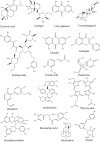
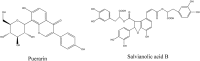
Ageing, an unanswered question in the medical field, is a multifactorial process that results in a progressive functional decline in cells, tissues and organisms. Although it is impossible to prevent ageing, slowing down the rate of ageing is entirely possible to achieve. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is characterized by the nourishing of life and its role in anti-ageing is getting more and more attention. This article summarizes the work done on the natural products from TCM that are reported to have anti-ageing effects, in the past two decades. The effective anti-ageing ingredients identified can be generally divided into flavonoids, saponins, polysaccharides, alkaloids and others. Astragaloside, Cistanche tubulosa acteoside, icariin, tetrahydrocurcumin, quercetin, butein, berberine, catechin, curcumin, epigallocatechin gallate, gastrodin, 6-Gingerol, glaucarubinone, ginsenoside Rg1, luteolin, icarisid II, naringenin, resveratrol, theaflavin, carnosic acid, catalpol, chrysophanol, cycloastragenol, emodin, galangin, echinacoside, ferulic acid, huperzine, honokiol, isoliensinine, phycocyanin, proanthocyanidins, rosmarinic acid, oxymatrine, piceid, puerarin and salvianolic acid B are specified in this review. Simultaneously, chemical structures of the monomers with anti-ageing activities are listed, and their source, model, efficacy and mechanism are also described. The TCMs with anti-ageing function are classified according to their action pathways, including the telomere and telomerase, the sirtuins, the mammalian target of rapamycin, AMP-activated kinase and insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 signalling pathway, free radicals scavenging and the resistance to DNA damage. Finally, Chinese compound prescription and extracts related to anti-ageing are introduced, which provides the basis and the direction for the further development of novel and potential drugs.
Linked articles: This article is part of a themed section on Principles of Pharmacological Research of Nutraceuticals. To view the other articles in this section visit http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bph.v174.11/issuetoc.
© 2016 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Allsopp RC, Harley CB (1995). Evidence for a critical telomere length in senescent human fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res 219: 130–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

