Hyaluronic acid fillers with cohesive polydensified matrix for soft-tissue augmentation and rejuvenation: a literature review
- PMID: 27660479
- PMCID: PMC5021061
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S106551
Hyaluronic acid fillers with cohesive polydensified matrix for soft-tissue augmentation and rejuvenation: a literature review
Abstract
Background: Cohesive monophasic polydensified fillers show unique viscoelastic properties and variable density of hyaluronic acid, allowing for a homogeneous tissue integration and distribution of the material.
Objective: The aim of this paper was to review the clinical data regarding the performance, tolerability, and safety of the Belotero(®) fillers for soft-tissue augmentation and rejuvenation.
Methods: A literature search was performed up until May 31, 2015 to identify all relevant articles on Belotero(®) fillers (Basic/Balance, Hydro, Soft, Intense, Volume) and equivalent products (Esthélis(®), Mesolis(®), Fortélis(®), Modélis(®)).
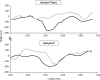
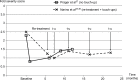
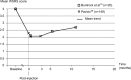
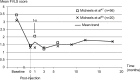
Results: This comprehensive review included 26 papers. Findings from three randomized controlled trials showed a greater reduction in nasolabial fold severity with Belotero(®) Basic/Balance than with collagen (at 8, 12, 16, and 24 weeks, n=118) and Restylane(®) (at 4 weeks, n=40), and higher patient satisfaction with Belotero(®) Intense than with Perlane(®) (at 2 weeks, n=20). With Belotero(®) Basic/Balance, an improvement of at least 1 point on the severity scale can be expected in ~80% of patients 1-6 months after injection, with an effect still visible at 8-12 months. Positive findings were also reported with Belotero(®) Volume (no reduction in hyaluronic acid volume at 12 months, as demonstrated by magnetic resonance imaging), Soft (improvement in the esthetic outcomes when used in a sequential approach), and Hydro (improvement in skin appearance in all patients). The most common adverse effects were mild-to-moderate erythema, edema, and hematoma, most of which were temporary. There were no reports of Tyndall effect, nodules, granulomas, or tissue necrosis.
Conclusion: Clinical evidence indicates sustainable esthetic effects, good safety profile, and long-term tolerability of the Belotero(®) fillers, particularly Belotero(®) Basic/Balance and Intense.
Keywords: CPM®; dermal filler; facial lines; filling; nasolabial fold; wrinkle.
Figures

References
-
- Carruthers J, Cohen SR, Joseph JH, Narins RS, Rubin M. The science and art of dermal fillers for soft-tissue augmentation. J Drugs Dermatol. 2009;8(4):335–350. - PubMed
-
- Palm MD. Filler frontier: what’s new and heading West to the US market. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2014;33(4):157–163. - PubMed
-
- International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (ISAPS) International survey on aesthetic/cosmetic procedures performed in 2013. 2014. [Accessed September 23, 2015]. Available from: http://www.isaps.org/Media/Default/global-statistics/2014%20ISAPS%20Resu....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

