miR-135b expression downregulates Ppm1e to activate AMPK signaling and protect osteoblastic cells from dexamethasone
- PMID: 27661114
- PMCID: PMC5342578
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.12138
miR-135b expression downregulates Ppm1e to activate AMPK signaling and protect osteoblastic cells from dexamethasone
Abstract
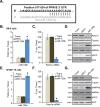
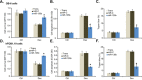
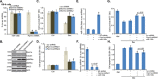
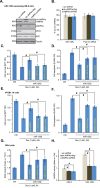
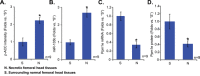
Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) could potently protect osteoblasts/osteoblastic cells from dexamethasone (Dex). We aim to induce AMPK activation via microRNA ("miRNA") downregulation of its phosphatase Ppm1e. We discovered that microRNA-135b ("miR-135b") targets the 3' untranslated regions (UTRs) of Ppm1e. In human osteoblasticOB-6 cells and hFOB1.19 cells, forced-expression of miR-135b downregulated Ppm1e and activated AMPK signaling. miR-135b also protected osteoblastic cells from Dex. shRNA-induced knockdown of Ppm1e similarly activated AMPK and inhibited Dex-induced damages. Intriguingly, in the Ppm1e-silenced osteoblastic cells, miR-135b expression failed to offer further cytoprotection against Dex. Notably, AMPK knockdown (via shRNA) or dominant negative mutation abolished miR-135b-induced AMPK activation and cytoprotection against Dex. Molecularly, miR-135b, via activating AMPK, increased nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) activity and inhibited Dex-induced oxidative stress. At last, we found that miR-135b level was increased in human necrotic femoral head tissues, which was correlated with Ppm1e downregulation and AMPK activation. There results suggest that miR-135b expression downregulates Ppm1e to activate AMPK signaling, which protects osteoblastic cells from Dex.
Keywords: AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK); dexamethasone (Dex); microRNA-135b; osteoblastic cells; phosphatase 1E (Ppm1e).
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interests were stated.
Figures
References
-
- Schacke H, Docke WD, Asadullah K. Mechanisms involved in the side effects of glucocorticoids. Pharmacol Ther. 2002;96:23–43. - PubMed
-
- Ding H, Wang T, Xu D, Cha B, Liu J, Li Y. Dexamethasone-induced apoptosis of osteocytic and osteoblastic cells is mediated by TAK1 activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;460:157–163. - PubMed
-
- Yun SI, Yoon HY, Jeong SY, Chung YS. Glucocorticoid induces apoptosis of osteoblast cells through the activation of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta. J Bone Miner Metab. 2009;27:140–148. - PubMed
-
- Ji F, Mao L, Liu Y, Cao X, Xie Y, Wang S, Fei H. K6PC-5, a novel sphingosine kinase 1 (SphK1) activator, alleviates dexamethasone-induced damages to osteoblasts through activating SphK1-Akt signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;458:568–575. - PubMed
-
- Fan JB, Liu W, Zhu XH, Yuan K, Xu DW, Chen JJ, Cui ZM. EGFR-AKT-mTOR activation mediates epiregulin-induced pleiotropic functions in cultured osteoblasts. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015;398:105–113. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

