Role of Glutamate and NMDA Receptors in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 27662322
- PMCID: PMC5791143
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-160763
Role of Glutamate and NMDA Receptors in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
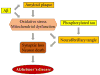
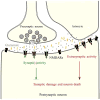
Excitatory glutamatergic neurotransmission via N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) is critical for synaptic plasticity and survival of neurons. However, excessive NMDAR activity causes excitotoxicity and promotes cell death, underlying a potential mechanism of neurodegeneration occurred in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Studies indicate that the distinct outcomes of NMDAR-mediated responses are induced by regionalized receptor activities, followed by different downstream signaling pathways. The activation of synaptic NMDARs initiates plasticity and stimulates cell survival. In contrast, the activation of extrasynaptic NMDARs promotes cell death and thus contributes to the etiology of AD, which can be blocked by an AD drug, memantine, an NMDAR antagonist that selectively blocks the function of extrasynaptic NMDARs.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; NMDA receptors; excitotoxicity; extrasynaptic NMDA receptors; glutamate; memantine.
Figures

References
-
- Abramov E, Dolev I, Fogel H, Ciccotosto GD, Ruff E, Slutsky I. Amyloid-beta as a positive endogenous regulator of release probability at hippocampal synapses. Nat Neurosci. 2009;12(12):1567–1576. - PubMed
-
- Alberdi E, Sanchez-Gomez MV, Cavaliere F, Perez-Samartin A, Zugaza JL, Trullas R, Domercq M, Matute C. Amyloid beta oligomers induce Ca2+ dysregulation and neuronal death through activation of ionotropic glutamate receptors. Cell Calcium. 2010;47(3):264–272. - PubMed
-
- Arias C, Arrieta I, Tapia R. beta-Amyloid peptide fragment 25–35 potentiates the calcium-dependent release of excitatory amino acids from depolarized hippocampal slices. J Neurosci Res. 1995;41(4):561–566. - PubMed
-
- Bleich S, Romer K, Wiltfang J, Kornhuber J. Glutamate and the glutamate receptor system: a target for drug action. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2003;18(Suppl 1):S33–40. - PubMed
-
- Bouvier M, Szatkowski M, Amato A, Attwell D. The glial cell glutamate uptake carrier countertransports pH-changing anions. Nature. 1992;360(6403):471–474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

