Characteristics of EEG Interpreters Associated With Higher Interrater Agreement
- PMID: 27662336
- PMCID: PMC5784780
- DOI: 10.1097/WNP.0000000000000344
Characteristics of EEG Interpreters Associated With Higher Interrater Agreement
Abstract
Purpose: The goal of the project is to determine characteristics of academic neurophysiologist EEG interpreters (EEGers), which predict good interrater agreement (IRA) and to determine the number of EEGers needed to develop an ideal standardized testing and training data set for epileptiform transient (ET) detection algorithms.
Methods: A three-phase scoring method was used. In phase 1, 19 EEGers marked the location of ETs in two hundred 30-second segments of EEG from 200 different patients. In phase 2, EEG events marked by at least 2 EEGers were annotated by 18 EEGers on a 5-point scale to indicate whether they were ETs. In phase 3, a third opinion was obtained from EEGers on any inconsistencies between phase 1 and phase 2 scoring.
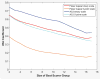
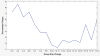
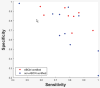
Results: The IRA for the 18 EEGers was only fair. A select group of the EEGers had good IRA and the other EEGers had low IRA. Board certification by the American Board of Clinical Neurophysiology was associated with better IRA performance but other board certifications, years of fellowship training, and years of practice were not. As the number of EEGers used for scoring is increased, the amount of change in the consensus opinion decreases steadily and is quite low as the group size approaches 10.
Conclusions: The IRA among EEGers varies considerably. The EEGers must be tested before use as scorers for ET annotation research projects. The American Board of Clinical Neurophysiology certification is associated with improved performance. The optimal size for a group of experts scoring ETs in EEG is probably in the 6 to 10 range.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Seidel S, Pablik E, Aull-Watschinger S, Seidl B, Pataraia E. Incidental epileptiform discharges in patients of a tertiary centre. Clin Neurophysiol. 2016;127:102–107. - PubMed
-
- van Donselaar CA, Schimsheimer RJ, Geerts AT, Declerck AC. Value of the electroencephalogram in adult patients with untreated idiopathic first seizures. Arch Neurol. 1992;49:231–237. - PubMed
-
- Fountain NB, Freeman JM. EEG is an essential clinical tool: pro and con. Epilepsia. 2006;47:23–25. - PubMed
-
- Halford JJ. Computerized epileptiform transient detection in scalp EEG: obstacles to progress and the example of computerized ECG interpretation. Clin Neurophysiol. 2009;120:1909–1915. - PubMed
-
- Benbadis SR. Errors in EEGs and the misdiagnosis of epilepsy: importance, causes, consequences, and proposed remedies. Epilepsy Behav. 2007;11:257–262. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

