Grp94 in complexes with IgG is a soluble diagnostic marker of gastrointestinal tumors and displays immune-stimulating activity on peripheral blood immune cells
- PMID: 27662661
- PMCID: PMC5341954
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.12141
Grp94 in complexes with IgG is a soluble diagnostic marker of gastrointestinal tumors and displays immune-stimulating activity on peripheral blood immune cells
Abstract
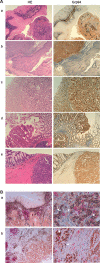
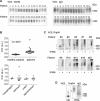
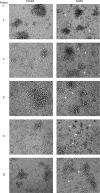
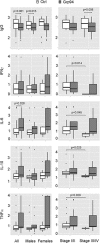
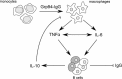
Glucose-regulated protein94 (Grp94), the most represented endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident heat shock protein (HSP), is a tumor antigen shared by different types of solid and hematological tumors. The tumor-specific feature of Grp94 is its translocation from the ER to the cell surface where it displays pro-oncogenic functions. This un-physiological location has important implications for both the tumor pathology and anti-tumor therapy. We wanted to address the question of whether Grp94 could be measured as liquid marker in cancer patients in order to make predictions of diagnostic and therapeutic relevance for the tumor. To this aim, we performed an in-depth investigation on patients with primary tumors of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, using different methodological approaches to detect Grp94 in tumor tissues, plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Results indicate that Grp94 is not only the antigen highly expressed in any tumor tissue and in cells of tumor infiltrates, mostly B lymphocytes, but it is also found in the circulation. However, the only form in which Grp94 was detected in the plasma of any patients and in B lymphocytes induced to proliferate, was that of stable complexes with Immunoglobulin (Ig)G. Using a specific immune-enzyme assay to measure plasma Grp94-IgG complexes, we showed that Grp94-IgG complexes were significantly increased in cancer patients compared to healthy control subjects, serving as diagnostic tumor biomarker. Results also demonstrate that the stimulation of patient PBMCs with Grp94-IgG complexes led to an increased secretion of inflammatory cytokines that might drive a potentially beneficial anti-tumor effect.
Keywords: biomarkers; gastrointestinal neoplasms; heat shock Proteins; immunoglobulins; immunomodulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of immunoglobulin secretion from peripheral blood mononuclear cells by glucose-regulated protein94 (Grp94) in allergic subjects.Mol Cell Biochem. 2012 Jun;365(1-2):47-52. doi: 10.1007/s11010-012-1242-x. Epub 2012 Jan 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22270544
-
Effects of glucose-regulated protein94 (Grp94) on Ig secretion from human blood mononuclear cells.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2011 May;16(3):329-38. doi: 10.1007/s12192-010-0245-3. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2011. PMID: 21120645 Free PMC article.
-
Stable complexes formed by Grp94 with human IgG promoting angiogenic differentiation of HUVECs by a cytokine-like mechanism.Mol Immunol. 2008 Aug;45(13):3639-48. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.04.020. Epub 2008 Jun 12. Mol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18554719
-
Cell Surface GRP94 as a Novel Emerging Therapeutic Target for Monoclonal Antibody Cancer Therapy.Cells. 2021 Mar 17;10(3):670. doi: 10.3390/cells10030670. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33802964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Endoplasmic Reticulum Chaperones at the Tumor Cell Surface and in the Extracellular Space].Klin Onkol. 2016 Fall;29 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):25-30. Klin Onkol. 2016. PMID: 27846717 Review. Czech.
Cited by
-
The HSP Immune Network in Cancer.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 30;12:796493. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.796493. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34917098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The overexpression of Hsp90B1 is associated with tumorigenesis of canine mammary glands.Mol Cell Biochem. 2018 Mar;440(1-2):23-31. doi: 10.1007/s11010-017-3152-4. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 28801701
-
GM2-GM3 gangliosides ratio is dependent on GRP94 through down-regulation of GM2-AP cofactor in brain metastasis cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 2;9(1):14241. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50761-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31578452 Free PMC article.
-
Bisubstrate-Type Chemical Probes Identify GRP94 as a Potential Target of Cytosine-Containing Adenosine Analogs.ACS Chem Biol. 2020 Apr 17;15(4):952-961. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.9b00965. Epub 2020 Apr 6. ACS Chem Biol. 2020. PMID: 32191434 Free PMC article.
-
GRP94 is an IGF-1R chaperone and regulates beta cell death in diabetes.Cell Death Dis. 2024 May 29;15(5):374. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06754-y. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38811543 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fu Z, Deng H, Wang X, Yang X, Wang Z, Liu L. Involvement of ER-alpha36 in the malignant growth of gastric carcinoma cells is associated with GRP94 overexpression. Histopathology. 2013;63:325–333. - PubMed
-
- Zheng HC, Takahashi H, Li XH, Hara T, Masuda S, Guan YF, Takano Y. Overexpression of GRP78 and GRP94 are markers for aggressive behavior and poor prognosis in gastric carcinomas. Hum Pathol. 2008;39:1042–1049. - PubMed
-
- Hu T, Xie N, Qin C, Wang J, You Y. Glucose-regulated protein 94 is a novel glioma biomarker and promotes the aggressiveness of glioma via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Tumour biology. 2015;36:9357–9364. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

