Feasibility, phase I, and phase II studies of tandutinib, an oral platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with recurrent glioblastoma
- PMID: 27663390
- PMCID: PMC5464374
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/now185
Feasibility, phase I, and phase II studies of tandutinib, an oral platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with recurrent glioblastoma
Abstract
Background: Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) signaling is important in gliomagenesis and PDGF receptor-β is expressed on most endothelial cells in glioblastoma specimens.
Methods: We report the results of feasibility, phase I, and phase II studies of tandutinib (MLN518), an orally bioavailable inhibitor of type III receptor tyrosine kinases including PDGF receptor-β, Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3, and c-Kit in patients with recurrent glioblastoma.
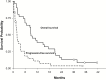
Results: In an initial feasibility study, 6 patients underwent resection for recurrent glioblastoma after receiving tandutinib 500mg twice daily for 7 days. The mean ratio of tandutinib concentration in brain tumor-to-plasma was 13.1±8.9 in 4 of the 6 patients. In the phase I study, 19 patients were treated at 500, 600, and 700mg twice daily dose levels. The maximum tolerated dose was found to be 600mg twice daily, and 30 patients were treated with this dose in the phase II study. The trial was closed after interim analysis, as the prespecified goal of patients alive and progression-free survival at 6 months was not achieved. Biomarker studies suggested that tandutinib treatment could lead to vascular disruption rather than normalization, which was associated with rapid progression.
Conclusions: Tandutinib readily distributed into the brain following oral administration and achieved concentrations within the tumor that exceed the corresponding concentration in plasma. The phase II study was closed at interim analysis due to lack of efficacy, although this study was not enriched for glioblastomas with alterations of the PDGF pathway.
Keywords: glioblastoma; overall survival; platelet-derived growth factor receptor; progression-free survival; tandutinib.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com
Figures
References
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(5):459–466. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):987–996. - PubMed
-
- Phillips HS, Kharbanda S, Chen R, et al. Molecular subclasses of high-grade glioma predict prognosis, delineate a pattern of disease progression, and resemble stages in neurogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2006;9(3):157–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous