Levodopa Effect on Basal Ganglia Motor Circuit in Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 27663605
- PMCID: PMC6492721
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.12634
Levodopa Effect on Basal Ganglia Motor Circuit in Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
Aims: To investigate the effects of levodopa on the basal ganglia motor circuit (BGMC) in Parkinson's disease (PD).
Methods: Thirty PD patients with asymmetrical bradykinesia and 30 control subjects were scanned using resting-state functional MRI. Functional connectivity of the BGMC was measured and compared before and after levodopa administration in patients with PD. The correlation between improvements in bradykinesia and changes in BGMC connectivity was examined.
Results: In the PD-off state (before medication), the posterior putamen and internal globus pallidus (GPi) had decreased connectivity while the subthalamic nucleus (STN) had enhanced connectivity within the BGMC relative to control subjects. Levodopa administration increased the connectivity of posterior putamen- and GPi-related networks but decreased the connectivity of STN-related networks. Improvements in bradykinesia were correlated with enhanced connectivity of the posterior putamen-cortical motor pathway and with decreased connectivity of the STN-thalamo-cortical motor pathway.
Conclusion: In PD patients with asymmetrical bradykinesia, levodopa can partially normalize the connectivity of the BGMC with a larger effect on the more severely affected side. Moreover, the beneficial effect of levodopa on bradykinesia is associated with normalization of the striato-thalamo-cortical motor and STN-cortical motor pathways. Our findings inform the neural mechanism of levodopa treatment in PD.
Keywords: Basal ganglia motor circuit; Bradykinesia; Connectivity; Levodopa; Parkinson's disease.
© 2016 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests to disclose.
Figures
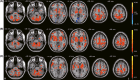
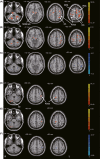
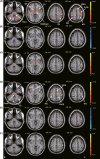
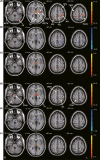
References
-
- Hauser RA. Levodopa: Past, present, and future. Eur Neurol 2009;62:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Haslinger B, Erhard P, Kampfe N, et al. Event‐related functional magnetic resonance imaging in Parkinson's disease before and after levodopa. Brain 2001;124:558–570. - PubMed
-
- Wu T, Hallett M. A functional MRI study of automatic movements in patients with Parkinson's disease. Brain 2005;128:2250–2259. - PubMed
-
- Wu T, Wang L, Hallett M, Chen Y, Li K, Chan P. Effective connectivity of brain networks during self‐initiated movement in Parkinson's disease. NeuroImage 2011;55:204–215. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

